Instant Connection for Pixel Streaming
— New Feature Automated Setup

Rhino 3D vs CATIA: Which Software Suits Your Design Needs Best?
Rhino 3D vs CATIA: Which Software Suits Your Design Needs Best?
Rhino 3D vs CATIA: Which Software Suits Your Design Needs Best?
Published on October 14, 2024
Updated on November 4, 2024
Table of Contents
When choosing a 3D CAD software, Rhino 3D and CATIA are two industry leaders, each excelling in different areas. Rhino 3D is known for its powerful tools in creative fields like architecture and product design, while CATIA dominates in technical sectors like aerospace and automotive engineering.
Picking the right tool for your project is crucial, as it impacts your workflow and final outcome. This guide will help beginners understand the key differences, strengths, and weaknesses of both software to make the right decision for their needs.
Accessing high-quality Rhino 3D Assets can elevate your projects, enhancing detail and saving time during the design process.
Overview of Rhino 3D and CATIA
Rhino 3D was developed by Robert McNeel & Associates and is popular for its versatility in creative industries like architecture, jewelry design, and product development. Its key feature is NURBS modeling, which allows designers to create freeform, organic shapes with precision. Rhino excels in projects requiring artistic flexibility and detailed surface modeling.
CATIA, created by Dassault Systèmes, is widely used in technical industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing. CATIA’s strength lies in parametric design, handling complex assemblies, simulations, and large-scale engineering tasks. It is the go-to software for precise, highly detailed engineering projects.
Looking for other comparisons? Rhino 3D might be a leading design tool, but exploring Rhino 3D Alternatives can open up new possibilities, especially if you're looking for specialized features.
User Interface & Learning Curve
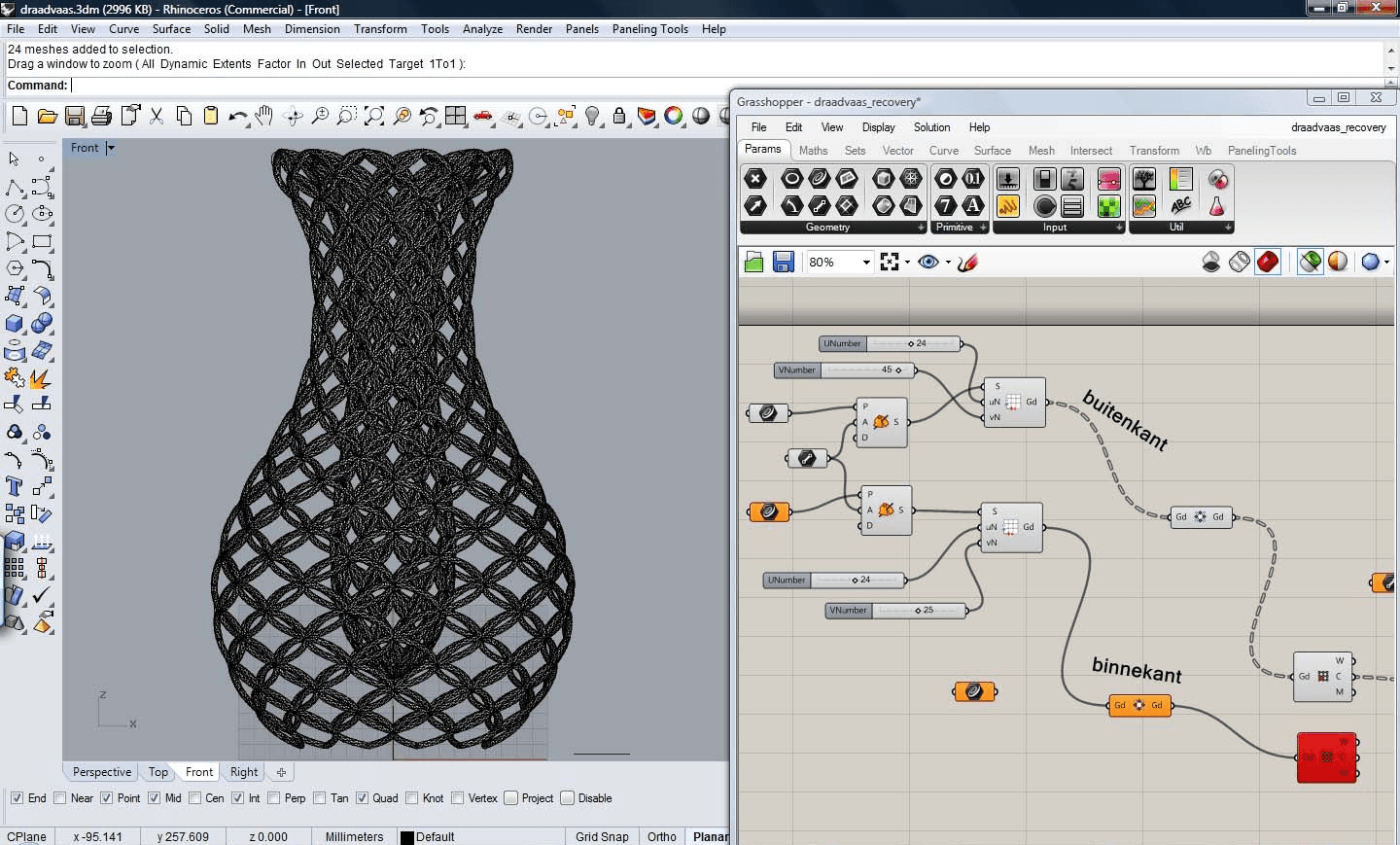
Rhino 3D offers a simple, intuitive interface that’s easy to navigate. It’s well-suited for beginners, especially designers focusing on creativity. The software’s customizable workflow allows users to dive into 3D modeling without being overwhelmed by technical details. Its learning curve is relatively shallow, making it a popular choice for creative professionals.
In contrast, CATIA features a more complex interface designed for engineering tasks. The software is robust but has a steep learning curve, requiring users to invest time in mastering its advanced tools. It’s ideal for experienced engineers working on intricate, large-scale projects.
Rhino is easier for users focused on design and creativity, while CATIA is best suited for those with a background in engineering, particularly in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is crucial.
Mastering Rhino 3D Keyboard Shortcuts can significantly speed up your workflow, allowing you to focus more on design and less on menu navigation.
Modeling Capabilities
Rhino 3D is known for its NURBS-based modeling, which allows for the creation of smooth, organic shapes and freeform designs. This makes it ideal for artistic and creative projects, such as architecture, jewelry, and product design. Rhino excels in flexibility and detailed surface modeling, giving designers full control over intricate shapes.
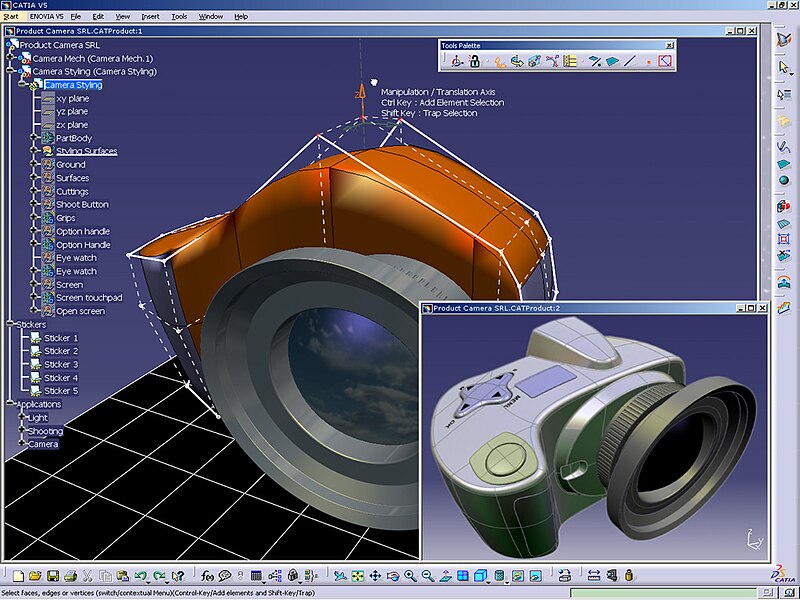
CATIA, on the other hand, is built for parametric modeling—a system that ensures precision and control in design. It’s perfect for engineering-driven projects, handling complex assemblies and simulations. CATIA is favored in industries like aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery, where accuracy and functionality are key.
Use Cases: Rhino’s strength lies in creative industries that prioritize design flexibility. Projects in architecture, product design, and fashion often benefit from Rhino’s organic modeling capabilities. CATIA is the go-to for engineering-heavy sectors like aerospace and automotive, where the need for precision and complex simulations is crucial.
Integrating the right Rhino 3D Plugins into your toolkit can unlock powerful features and add flexibility to your design capabilities.
Industry Applications
Rhino 3D is widely used in architecture, product design, fashion, and jewelry. Its ability to create complex, organic forms makes it perfect for industries where aesthetics are crucial. For example, architects use Rhino for designing buildings with flowing curves, while jewelry designers create intricate custom pieces. Rhino’s flexibility allows product designers to experiment with new shapes and forms, making it a go-to tool for creative professionals.
CATIA dominates in aerospace, automotive, and large-scale manufacturing. Aerospace engineers use CATIA to design aircraft components with precision, ensuring performance and safety. In the automotive industry, CATIA helps design entire vehicles, from the exterior body to the intricate parts inside. Manufacturing companies rely on CATIA for its ability to handle large, complex assemblies and ensure that all components work seamlessly together.
Rhino 3D shines in industries focused on creative expression and form, like architecture and fashion, while CATIA is better suited for industries that require engineering precision and handling of complex systems, such as aerospace and automotive. Each software is preferred by industries that prioritize either design flexibility (Rhino) or precision engineering (CATIA).
Whether you're a beginner or looking to refine your skills, the Best Rhino 3D Courses can provide valuable insights and hands-on learning opportunities.
Performance and Hardware Requirements
Rhino 3D can run efficiently on moderate hardware. Its lower system requirements make it accessible for freelancers, small teams, and design studios with limited resources. Rhino’s performance is smooth, even on less powerful machines, making it a flexible choice for creatives working on smaller projects.
Choosing the right hardware can significantly impact your Rhino 3D experience; explore the Best Computers for Rhino 3D, optimized for handling complex designs.
CATIA is more demanding in terms of hardware. It’s designed for large-scale, data-heavy engineering projects that require powerful computing resources. The software handles complex simulations and large assemblies, which makes it suitable for industries like aerospace and automotive but requires high-end hardware to run smoothly.
Rhino’s performance excels in small to medium-scale projects, offering accessibility to a wider audience. CATIA, however, is built for high-performance needs and is best suited for large-scale, complex engineering projects where powerful hardware is available.
Comparing Rhino 3D vs Fusion 360 reveals their unique strengths, making it easier to select the software that aligns with your project goals.
Collaboration and Integration
Rhino 3D offers great flexibility, integrating with a wide range of plugins and third-party software like Grasshopper, V-Ray, and others. This makes it adaptable for various creative workflows and design processes. Users can easily customize Rhino to fit their specific needs.
CATIA excels in collaboration for large engineering teams. It features strong tools for version control, multi-disciplinary collaboration, and real-time teamwork. CATIA’s suite of integrated tools makes it ideal for managing complex projects across various departments.
Rhino is better for smaller teams with varied workflows, while CATIA is superior for large, cross-functional teams in engineering-heavy industries. Furthermore, Running Rhino 3D on a Cloud Computer gives you the freedom to work from virtually anywhere with high processing power.
Cost and Licensing
Rhino 3D offers a relatively affordable one-time payment model, which makes it a great option for freelancers and small design teams. Once purchased, there are no ongoing fees, which provides long-term savings for smaller businesses or individual designers.
CATIA, however, uses a subscription-based licensing model with higher costs. This pricing structure is designed for large enterprises that require comprehensive tools and support for complex engineering projects.
Rhino is the more cost-effective choice for those on a budget, while CATIA’s higher cost suits large companies with extensive needs.
For those deciding between Rhino 3D vs SketchUp, understanding their differences can help you choose the best tool for your design needs.
Summary of Pros and Cons
Rhino 3D offers creative freedom and is affordable, making it perfect for artistic projects like architecture, product design, and jewelry. However, it is less suited for heavy engineering tasks that require advanced simulations or parametric modeling.
CATIA excels in precision and handles large-scale engineering projects with its robust toolset. However, its higher cost and steep learning curve can be barriers, especially for smaller teams.
Conclusion: Choose Rhino for creative, design-focused projects. Opt for CATIA when dealing with complex, engineering-heavy tasks.
Working in Rhino 3D can sometimes be interrupted by unexpected crashes; knowing the most Common Rhino 3D Crashes and How to Fix Them can save you time and frustration.
Conclusion & Final Recommendations
Both Rhino 3D and CATIA are excellent tools, but they serve different needs. Rhino 3D is perfect for designers in creative fields like architecture, jewelry, and product design, offering flexibility and affordability. CATIA, on the other hand, is best suited for industries requiring precision, such as aerospace, automotive, and large-scale engineering.
Ultimately, your choice depends on your project’s complexity and industry. Evaluate your needs—whether it’s creative freedom or engineering precision—and choose the software that aligns with your workflow.
If you're looking to improve your workflow, learning How to Render Faster on Rhinoceros could be a game-changer for productivity and visual quality.
FAQs:
Which software is easier to learn for a beginner?
Rhino 3D is easier to learn due to its intuitive interface and focus on design. CATIA has a steeper learning curve, ideal for users with engineering backgrounds.
Can I use Rhino 3D for engineering projects?
Rhino can handle light engineering tasks but lacks the precision and advanced simulation tools that CATIA offers for large-scale engineering.
Which is better for architecture, Rhino or CATIA?
Rhino is preferred for architectural design due to its ability to model organic shapes and creative forms.
Is CATIA better for large teams?
Yes, CATIA is designed for large-scale projects and collaboration, with robust tools for managing complex assemblies and teamwork.
What are the cost differences between Rhino and CATIA?
Rhino offers a one-time purchase, making it more affordable for small teams and freelancers, while CATIA’s subscription model is costlier, geared toward enterprises.
Can Rhino and CATIA be used together in a project?
Yes, Rhino can handle the creative design phase, while CATIA manages detailed engineering tasks. Many teams use them in tandem for different project stages.
When choosing a 3D CAD software, Rhino 3D and CATIA are two industry leaders, each excelling in different areas. Rhino 3D is known for its powerful tools in creative fields like architecture and product design, while CATIA dominates in technical sectors like aerospace and automotive engineering.
Picking the right tool for your project is crucial, as it impacts your workflow and final outcome. This guide will help beginners understand the key differences, strengths, and weaknesses of both software to make the right decision for their needs.
Accessing high-quality Rhino 3D Assets can elevate your projects, enhancing detail and saving time during the design process.
Overview of Rhino 3D and CATIA
Rhino 3D was developed by Robert McNeel & Associates and is popular for its versatility in creative industries like architecture, jewelry design, and product development. Its key feature is NURBS modeling, which allows designers to create freeform, organic shapes with precision. Rhino excels in projects requiring artistic flexibility and detailed surface modeling.
CATIA, created by Dassault Systèmes, is widely used in technical industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing. CATIA’s strength lies in parametric design, handling complex assemblies, simulations, and large-scale engineering tasks. It is the go-to software for precise, highly detailed engineering projects.
Looking for other comparisons? Rhino 3D might be a leading design tool, but exploring Rhino 3D Alternatives can open up new possibilities, especially if you're looking for specialized features.
User Interface & Learning Curve

Rhino 3D offers a simple, intuitive interface that’s easy to navigate. It’s well-suited for beginners, especially designers focusing on creativity. The software’s customizable workflow allows users to dive into 3D modeling without being overwhelmed by technical details. Its learning curve is relatively shallow, making it a popular choice for creative professionals.
In contrast, CATIA features a more complex interface designed for engineering tasks. The software is robust but has a steep learning curve, requiring users to invest time in mastering its advanced tools. It’s ideal for experienced engineers working on intricate, large-scale projects.
Rhino is easier for users focused on design and creativity, while CATIA is best suited for those with a background in engineering, particularly in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is crucial.
Mastering Rhino 3D Keyboard Shortcuts can significantly speed up your workflow, allowing you to focus more on design and less on menu navigation.
Modeling Capabilities
Rhino 3D is known for its NURBS-based modeling, which allows for the creation of smooth, organic shapes and freeform designs. This makes it ideal for artistic and creative projects, such as architecture, jewelry, and product design. Rhino excels in flexibility and detailed surface modeling, giving designers full control over intricate shapes.

CATIA, on the other hand, is built for parametric modeling—a system that ensures precision and control in design. It’s perfect for engineering-driven projects, handling complex assemblies and simulations. CATIA is favored in industries like aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery, where accuracy and functionality are key.
Use Cases: Rhino’s strength lies in creative industries that prioritize design flexibility. Projects in architecture, product design, and fashion often benefit from Rhino’s organic modeling capabilities. CATIA is the go-to for engineering-heavy sectors like aerospace and automotive, where the need for precision and complex simulations is crucial.
Integrating the right Rhino 3D Plugins into your toolkit can unlock powerful features and add flexibility to your design capabilities.
Industry Applications
Rhino 3D is widely used in architecture, product design, fashion, and jewelry. Its ability to create complex, organic forms makes it perfect for industries where aesthetics are crucial. For example, architects use Rhino for designing buildings with flowing curves, while jewelry designers create intricate custom pieces. Rhino’s flexibility allows product designers to experiment with new shapes and forms, making it a go-to tool for creative professionals.
CATIA dominates in aerospace, automotive, and large-scale manufacturing. Aerospace engineers use CATIA to design aircraft components with precision, ensuring performance and safety. In the automotive industry, CATIA helps design entire vehicles, from the exterior body to the intricate parts inside. Manufacturing companies rely on CATIA for its ability to handle large, complex assemblies and ensure that all components work seamlessly together.
Rhino 3D shines in industries focused on creative expression and form, like architecture and fashion, while CATIA is better suited for industries that require engineering precision and handling of complex systems, such as aerospace and automotive. Each software is preferred by industries that prioritize either design flexibility (Rhino) or precision engineering (CATIA).
Whether you're a beginner or looking to refine your skills, the Best Rhino 3D Courses can provide valuable insights and hands-on learning opportunities.
Performance and Hardware Requirements
Rhino 3D can run efficiently on moderate hardware. Its lower system requirements make it accessible for freelancers, small teams, and design studios with limited resources. Rhino’s performance is smooth, even on less powerful machines, making it a flexible choice for creatives working on smaller projects.
Choosing the right hardware can significantly impact your Rhino 3D experience; explore the Best Computers for Rhino 3D, optimized for handling complex designs.

CATIA is more demanding in terms of hardware. It’s designed for large-scale, data-heavy engineering projects that require powerful computing resources. The software handles complex simulations and large assemblies, which makes it suitable for industries like aerospace and automotive but requires high-end hardware to run smoothly.
Rhino’s performance excels in small to medium-scale projects, offering accessibility to a wider audience. CATIA, however, is built for high-performance needs and is best suited for large-scale, complex engineering projects where powerful hardware is available.
Comparing Rhino 3D vs Fusion 360 reveals their unique strengths, making it easier to select the software that aligns with your project goals.
Collaboration and Integration

Rhino 3D offers great flexibility, integrating with a wide range of plugins and third-party software like Grasshopper, V-Ray, and others. This makes it adaptable for various creative workflows and design processes. Users can easily customize Rhino to fit their specific needs.
CATIA excels in collaboration for large engineering teams. It features strong tools for version control, multi-disciplinary collaboration, and real-time teamwork. CATIA’s suite of integrated tools makes it ideal for managing complex projects across various departments.
Rhino is better for smaller teams with varied workflows, while CATIA is superior for large, cross-functional teams in engineering-heavy industries. Furthermore, Running Rhino 3D on a Cloud Computer gives you the freedom to work from virtually anywhere with high processing power.
Cost and Licensing
Rhino 3D offers a relatively affordable one-time payment model, which makes it a great option for freelancers and small design teams. Once purchased, there are no ongoing fees, which provides long-term savings for smaller businesses or individual designers.
CATIA, however, uses a subscription-based licensing model with higher costs. This pricing structure is designed for large enterprises that require comprehensive tools and support for complex engineering projects.
Rhino is the more cost-effective choice for those on a budget, while CATIA’s higher cost suits large companies with extensive needs.
For those deciding between Rhino 3D vs SketchUp, understanding their differences can help you choose the best tool for your design needs.
Summary of Pros and Cons
Rhino 3D offers creative freedom and is affordable, making it perfect for artistic projects like architecture, product design, and jewelry. However, it is less suited for heavy engineering tasks that require advanced simulations or parametric modeling.
CATIA excels in precision and handles large-scale engineering projects with its robust toolset. However, its higher cost and steep learning curve can be barriers, especially for smaller teams.
Conclusion: Choose Rhino for creative, design-focused projects. Opt for CATIA when dealing with complex, engineering-heavy tasks.
Working in Rhino 3D can sometimes be interrupted by unexpected crashes; knowing the most Common Rhino 3D Crashes and How to Fix Them can save you time and frustration.
Conclusion & Final Recommendations
Both Rhino 3D and CATIA are excellent tools, but they serve different needs. Rhino 3D is perfect for designers in creative fields like architecture, jewelry, and product design, offering flexibility and affordability. CATIA, on the other hand, is best suited for industries requiring precision, such as aerospace, automotive, and large-scale engineering.
Ultimately, your choice depends on your project’s complexity and industry. Evaluate your needs—whether it’s creative freedom or engineering precision—and choose the software that aligns with your workflow.
If you're looking to improve your workflow, learning How to Render Faster on Rhinoceros could be a game-changer for productivity and visual quality.
FAQs:
Which software is easier to learn for a beginner?
Rhino 3D is easier to learn due to its intuitive interface and focus on design. CATIA has a steeper learning curve, ideal for users with engineering backgrounds.
Can I use Rhino 3D for engineering projects?
Rhino can handle light engineering tasks but lacks the precision and advanced simulation tools that CATIA offers for large-scale engineering.
Which is better for architecture, Rhino or CATIA?
Rhino is preferred for architectural design due to its ability to model organic shapes and creative forms.
Is CATIA better for large teams?
Yes, CATIA is designed for large-scale projects and collaboration, with robust tools for managing complex assemblies and teamwork.
What are the cost differences between Rhino and CATIA?
Rhino offers a one-time purchase, making it more affordable for small teams and freelancers, while CATIA’s subscription model is costlier, geared toward enterprises.
Can Rhino and CATIA be used together in a project?
Yes, Rhino can handle the creative design phase, while CATIA manages detailed engineering tasks. Many teams use them in tandem for different project stages.
Get Beyond Your Computer Performance
Run applications on your cloud computer with the latest generation hardware. No more crashes or lags.

Trial includes 1 hour usage + 7 days of storage.
Get Beyond Your Computer Performance
Run applications on your cloud computer with the latest generation hardware. No more crashes or lags.

Trial includes 1 hour usage + 7 days of storage.

Ready to focus on your creativity?
Vagon gives you the ability to create & render projects, collaborate, and stream applications with the power of the best hardware.

Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
How to Use SolidWorks for 3D Printing: STL Export, Settings & Workflow Guide
How to Use Rhino3D for 3D Printing: A Complete Guide to STL, Meshes, and Printable Geometry
Best VMware Horizon Alternatives for VDI Teams in 2026
Top Citrix Alternatives in 2026
Top Azure Virtual Desktop Alternatives in 2026
Best Laptops of 2026: What Actually Matters
Best 3D Printers in 2026: Honest Picks, Real Use Cases
Best AI Productivity Tools in 2026: Build a Smarter Workflow
Best AI Presentation Tools in 2026: What Actually Works
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
How to Use SolidWorks for 3D Printing: STL Export, Settings & Workflow Guide
How to Use Rhino3D for 3D Printing: A Complete Guide to STL, Meshes, and Printable Geometry
Best VMware Horizon Alternatives for VDI Teams in 2026
Top Citrix Alternatives in 2026
Top Azure Virtual Desktop Alternatives in 2026
Best Laptops of 2026: What Actually Matters
Best 3D Printers in 2026: Honest Picks, Real Use Cases
Best AI Productivity Tools in 2026: Build a Smarter Workflow
Best AI Presentation Tools in 2026: What Actually Works
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
How to Use SolidWorks for 3D Printing: STL Export, Settings & Workflow Guide
How to Use Rhino3D for 3D Printing: A Complete Guide to STL, Meshes, and Printable Geometry
Best VMware Horizon Alternatives for VDI Teams in 2026
Top Citrix Alternatives in 2026
Top Azure Virtual Desktop Alternatives in 2026
Best Laptops of 2026: What Actually Matters
Best 3D Printers in 2026: Honest Picks, Real Use Cases
Best AI Productivity Tools in 2026: Build a Smarter Workflow
Best AI Presentation Tools in 2026: What Actually Works
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog


