Instant Connection for Pixel Streaming
— New Feature Automated Setup

Top VR Technologies And Trends To Watch In 2025
Top VR Technologies And Trends To Watch In 2025
Top VR Technologies And Trends To Watch In 2025
Published on May 7, 2025
Table of Contents
Virtual Reality (VR) has rapidly evolved from niche gaming tech into a mainstream tool reshaping industries in 2025. Thanks to lighter headsets, sharper displays, and more affordable pricing, VR is now used for far more than entertainment.
Today, architects walk through virtual buildings before construction begins. Students explore historical sites in digital classrooms. Remote teams collaborate in virtual offices, while doctors practice surgeries in immersive simulations. VR has become a platform for real-world problem-solving, not just play.
This transformation is driven not only by hardware but also by new technologies like generative AI, spatial computing, and cloud VR streaming. Platforms such as Vagon Streams now allow users to access powerful VR applications directly from the cloud, removing the need for expensive PCs or bulky equipment.
As VR adoption grows, expectations around user experience, accessibility, and content performance are also shifting. In this post, we’ll explore the key VR trends in 2025 that are shaping the future of immersive tech — and how creators, educators, and professionals can benefit.
#1. Hardware Innovations and Accessibility
The growth of virtual reality in 2025 is tightly linked to the evolution of VR hardware. Devices are not only getting more powerful, but also more accessible, comfortable, and affordable. These changes are crucial for bringing immersive experiences to a wider audience.
Lighter, Sharper, Smarter Headsets
In recent years, VR headsets have made a significant leap in performance and design. Devices like the Meta Quest 3 and Apple Vision Pro have raised the bar with higher-resolution displays, better depth tracking, and streamlined form factors. Advanced lenses, micro-OLED screens, and inside-out tracking systems have become the new standard, offering sharper visuals without the bulk.
Comfort has also become a focus. Manufacturers are prioritizing weight distribution, airflow, and adjustable fittings, making it easier to spend extended time in VR without fatigue. Battery life and wireless connectivity have improved as well, giving users more freedom to move.
These improvements are especially important for industries using VR in training, education, or design, places where long sessions and high precision are the norm.

Affordability Expands the Market
VR is becoming more accessible not just in form, but in cost. As production scales and competition grows, entry-level headsets with solid performance are now available at prices once unthinkable. This shift is opening up VR to students, independent creators, and small businesses.
At the same time, cloud-powered streaming platforms like Vagon Streams are removing the need for high-end local hardware altogether. By offloading the compute load to the cloud, users can run intensive VR applications from lightweight devices, even older laptops or standalone headsets.
Smart Glasses and Wearables
While full VR headsets are advancing, lightweight alternatives are emerging fast. Smart glasses and XR (extended reality) wearables now bridge the gap between virtual and real. Devices like Meta’s Ray-Ban Stories or Google’s Project Astra blend audio, visual cues, and spatial awareness into sleek, glasses-style hardware.
These wearables allow users to interact with digital content without losing connection to their physical environment. For everyday tasks, remote assistance, or hybrid collaboration, they offer a compelling mix of utility and minimalism.

The Bottom Line
In 2025, hardware is no longer a barrier for most VR users. Whether through affordable headsets, sleek smart glasses, or cloud streaming, accessing immersive content is easier than ever. This broader reach is helping VR expand into new industries and use cases, and setting the stage for the next wave of innovation.
As VR hardware continues to advance, creators are seeing a whole new world of possibilities. If you're diving into VR development, it's essential to understand how software like Blender for Virtual Reality can enhance your creations.
#2. AI Integration Enhancing VR Experiences
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the most powerful forces accelerating VR’s evolution in 2025. As VR environments grow more complex and personalized, AI is playing a key role in shaping how users interact with virtual worlds, and how those worlds are created.
Personalized Content and Smarter Interactions
One of the most visible impacts of AI in VR is personalization. Machine learning algorithms now adapt virtual environments to individual users in real time. Whether it’s adjusting the difficulty level in a VR training session, modifying a learning path in an educational simulation, or fine-tuning narrative pacing in a VR game, AI makes the experience feel more tailored and responsive.
AI-driven avatars are also becoming more lifelike. Voice synthesis and natural language processing allow NPCs (non-player characters) and virtual assistants to understand and respond to users with realistic tone and behavior, creating smoother, more engaging interactions.
This is especially important in education, therapy, and collaborative platforms, where feeling “understood” by the system boosts effectiveness and comfort.

Generative AI and Dynamic Worldbuilding
AI isn’t just improving how we use VR, it’s also changing how VR content is built. With the rise of generative AI, creators can design environments, objects, and entire scenarios faster than ever.
Instead of manually modeling every element, developers can now describe a scene in simple terms and let AI generate 3D assets or animations. This speeds up production and makes worldbuilding more accessible to smaller teams and independent creators.
Some platforms even use AI to generate environments on-the-fly during gameplay or interaction, allowing for adaptive storytelling and unique user journeys.
Smarter Hardware and Wearables
AI also powers the next generation of smart wearables. For instance, Meta’s Ray-Ban smart glasses now include AI capabilities that allow users to ask questions about what they see in real time, essentially turning their view into an interactive experience.
On a broader level, these AI features help streamline user interfaces. Instead of relying on complex menus or manual controls, users can interact with VR systems through natural language, gestures, or even gaze tracking, all interpreted by intelligent algorithms.

Why It Matters
AI and VR are converging fast, creating immersive environments that feel intelligent, adaptive, and uniquely personal. For creators, this means faster content production and smarter tools. For users, it means more engaging and seamless experiences.
And when paired with cloud infrastructure, like Vagon Streams, AI-powered VR doesn’t have to be limited by local computing power. Heavy processing can happen in the cloud, with results streamed directly to your device, making high-performance AI in VR accessible to more people.
With AI’s growing role in VR, we’re entering a phase of smarter, more adaptive virtual environments. To create realistic AI-driven content, developers should explore tools and resources in the VR space, such as those discussed in our article on top graphics cards for VR, which are key for achieving higher-quality AI interactions in virtual worlds.
#3. Enterprise and Industrial Applications
Virtual reality is no longer confined to entertainment or niche research labs. In 2025, VR is firmly established as a serious tool across enterprise sectors, from retail and manufacturing to healthcare and education. VR is also transforming retail logistics—when combined with advanced 3PL WMS solutions, it enables virtual walkthroughs and real-time training that help optimize inventory handling and streamline supply chain operations.
VR for Training and Simulation
One of the strongest use cases for VR in industry is workforce training. Simulations in VR offer a safe, repeatable, and measurable environment for employees to learn and practice skills. Sectors like retail, aviation, energy, and emergency response now use VR to prepare staff for real-world scenarios without real-world risks.
Walmart, for example, uses VR to train employees on customer service, holiday rush prep, and emergency protocols. In healthcare, hospitals simulate surgeries or high-stress environments to prepare medical staff without involving real patients.
These training programs are not only safer, they’re also more scalable. With cloud-based platforms like Vagon Streams, large teams can access the same immersive modules from different locations, without requiring expensive local setups.

Healthcare and Therapy
VR is making a growing impact in medicine as well. Surgeons use VR for pre-operative planning and fine-tuning procedures in 3D environments that mimic real anatomy. Therapists use VR exposure therapy to help patients with PTSD, anxiety, or phobias by gradually introducing controlled stimuli in a safe setting. In parallel, healthcare wearable app development is enabling real-time monitoring and feedback, making these immersive treatments even more data-driven and personalized.
Additionally, VR is being used for rehabilitation, offering patients interactive exercises that help them regain mobility or cognitive function in a gamified, trackable format.
These applications rely on realism, responsiveness, and accessibility, traits made more viable when combined with AI and cloud infrastructure.

Prototyping, Design, and Collaboration
VR is also revolutionizing product development. Designers and engineers can build and test prototypes in virtual environments before committing to physical production. This is already in use by companies like BMW, which has created virtual factories using tools like NVIDIA’s Omniverse to simulate and optimize workflows before they go live.
Architects and construction teams walk through buildings in VR before a single brick is laid. Industrial designers iterate on product concepts more quickly using immersive modeling tools. And with VR collaboration spaces, teams spread across continents can meet inside the same virtual workspace, examine 3D models together, and make decisions in real time.
This ability to collaborate inside immersive environments is particularly powerful when paired with cloud streaming. Even team members with minimal hardware can join and contribute through platforms like Vagon Streams.
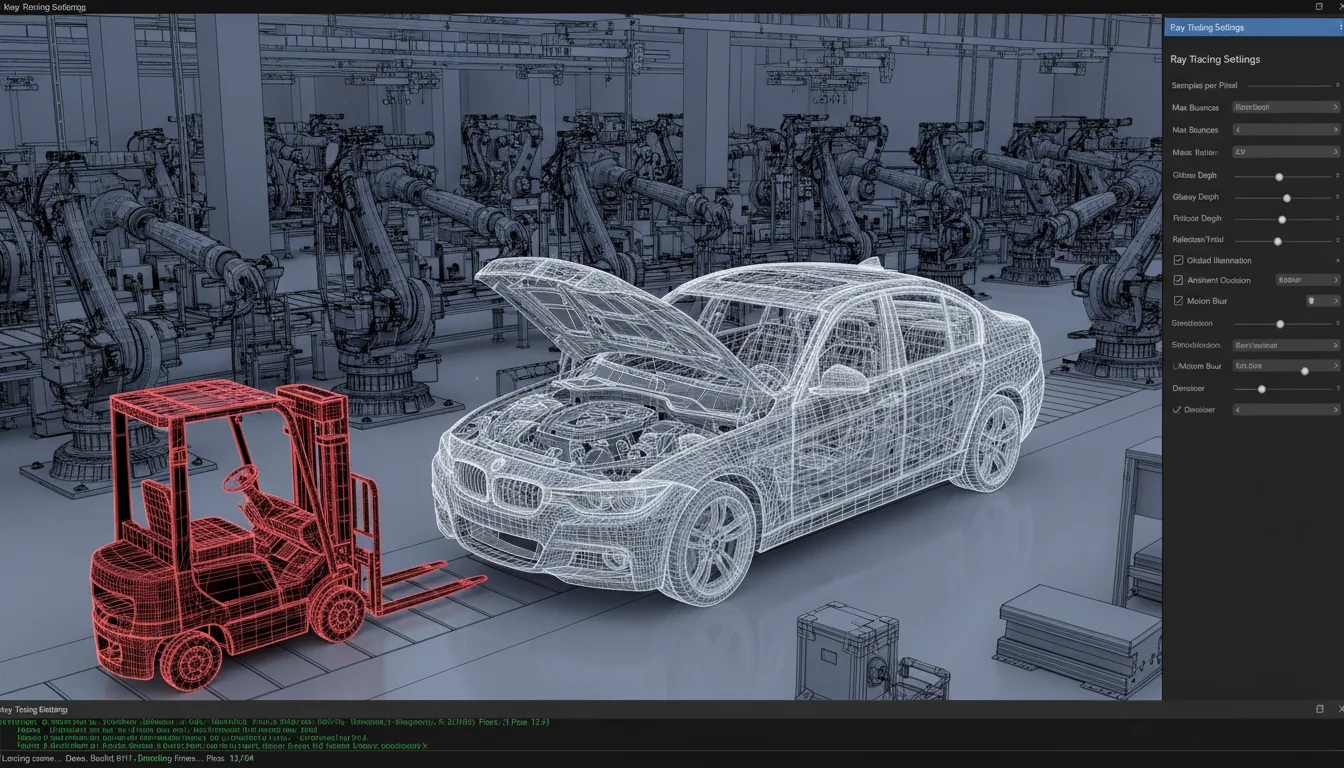
A Strategic Investment
For enterprises, VR is no longer a gamble, it’s a strategic investment. The technology reduces costs, increases safety, speeds up innovation cycles, and opens up new collaboration models. Cloud streaming platforms like Vagon Streams support this by lowering the technical entry barrier, making immersive work tools available on a broader range of devices.
As organizations continue to digitize workflows, VR is proving to be more than just a novelty. It’s a core part of the industrial and professional tech stack.
#4. Evolution of VR in Entertainment and Social Interaction
Entertainment helped virtual reality find its first audience, and in 2025, it’s still one of the most vibrant areas for innovation. But the definition of “VR entertainment” has evolved. It’s no longer just about games, it’s about social connection, shared experiences, and immersive storytelling that blurs the line between fiction and reality.
Next-Generation VR Gaming
Gaming continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in VR. Today’s titles offer expansive, interactive worlds, sophisticated physics, and multiplayer modes that make players feel truly present. Haptic feedback suits, motion tracking, and eye-tracking features are becoming more common, letting players feel resistance when they pull a bowstring or interact with objects in 3D space.
Developers are also leaning into procedural generation and adaptive AI to create dynamic, personalized game environments. This means no two sessions are exactly the same, and players are rewarded with deeper immersion and longer engagement.
As high-fidelity gaming becomes more compute-intensive, cloud streaming is playing a bigger role. Platforms like Vagon Streams let users run demanding VR games without needing a gaming PC, just a stable connection and a lightweight headset.

Immersive Storytelling
Filmmakers and artists are also turning to VR to tell stories in new ways. Unlike traditional cinema, VR places the viewer inside the narrative. You’re not watching from a distance, you’re surrounded by the story.
Interactive films, 360° documentaries, and virtual theater are gaining traction, offering creators a new palette of tools. Audiences, in turn, enjoy richer and more emotionally resonant experiences.
As creators experiment with these formats, cloud tools are once again reducing barriers. With heavy rendering handled remotely, artists can focus on creative direction, even on modest devices.
Virtual Social Worlds
Beyond games, VR is changing how we socialize. Platforms like VRChat, Horizon Worlds, and Rec Room have become digital gathering spaces where people meet, collaborate, and even perform together in real time. Users attend concerts, host workshops, or just hang out in shared 3D spaces, with a growing focus on self-expression through customizable avatars and environments.
These spaces are becoming more important in an era of hybrid and remote living. VR makes distance feel smaller, offering a level of presence that traditional video calls can’t match.
Still, developers are working to improve accessibility, moderation tools, and user safety. These social environments need clear guidelines and thoughtful design to ensure they remain inclusive and healthy spaces.

A More Connected Future
Entertainment and social interaction are driving mainstream adoption of VR. But they’re also pushing the medium forward, introducing more expressive tools, deeper engagement, and more human experiences. With hardware improving and cloud platforms making VR more accessible, 2025 is a turning point in how we connect, create, and escape together.
For creators looking to take their VR gaming or interactive experiences to the next level, understanding the tools and platforms available is crucial. Check out our tips for creating VR in Unreal Engine to help bring your VR visions to life.
#5. Emergence of Mixed Reality and Spatial Computing
In 2025, the lines between physical and virtual spaces are becoming increasingly blurred. Thanks to major strides in mixed reality (MR) and spatial computing, users are no longer just inside virtual environments, they’re interacting with digital content layered directly onto their physical world. This convergence is unlocking new possibilities in productivity, design, education, and everyday life.
What is Mixed Reality?
Mixed reality sits between traditional VR and augmented reality (AR). It merges real-world and digital elements into a single, interactive space. Unlike VR, which fully immerses you in a virtual environment, MR allows digital content to respond to the physical world in real time.
Devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Microsoft HoloLens 2 are leading the charge. These headsets can place a 3D model on your actual desk or let you manipulate digital controls floating in your living room. The key is spatial awareness, these systems understand the geometry of your environment and adapt virtual content accordingly.

Rise of Spatial Computing
Spatial computing takes this further. It refers to the ability of machines to understand and respond to the physical world using sensors, cameras, and AI. Spatial computing powers gesture recognition, room-scale mapping, and eye-tracking, turning your environment into an interface.
This means users can walk around a digital object, resize it with their hands, or glance at a control panel to activate it. Architects can review building models inside the construction site. Teachers can turn a classroom into a living solar system. Product teams can brainstorm using virtual whiteboards in shared space, without being in the same location.
These experiences are no longer just futuristic demos. They’re being deployed in real workflows across education, industrial design, and healthcare.
Making MR More Accessible
Historically, MR and spatial computing required powerful hardware and dedicated environments. But with cloud streaming, that’s changing fast. Complex spatial applications can now run remotely and be delivered to lightweight headsets or even tablets.
For example, with Vagon Streams, professionals can access MR design tools or spatial simulations from wherever they are, no need for a high-end local machine. This flexibility expands the reach of mixed reality beyond enterprise labs into classrooms, studios, and homes.
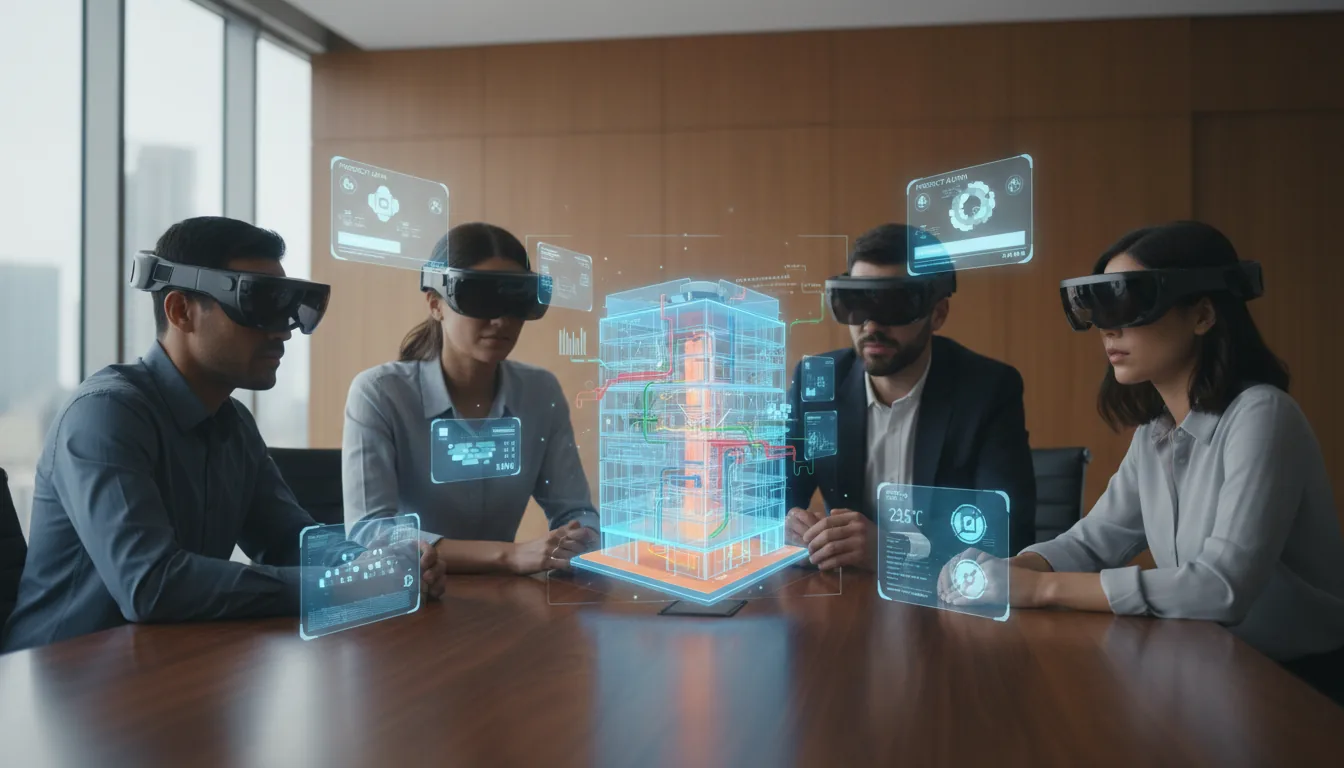

A Shift in How We Work and Learn
The biggest impact of MR and spatial computing is how it transforms interaction. Instead of using a mouse or touchpad, people are using movement, space, and presence to engage with digital content. This makes technology more intuitive, and potentially more inclusive.
As spatial computing becomes more integrated into daily workflows, we’ll see a shift toward environments that feel more human and immersive. And with cloud infrastructure reducing the technical barriers, we’re entering an era where physical and digital aren’t separate, they’re merged.

#6. Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
As we look beyond 2025, virtual reality continues to evolve in ways that extend far beyond headsets and entertainment. The next wave of innovation is about deeper integration, smarter systems, and a more seamless blend between the physical and digital worlds. Here are some of the key trends shaping the future of VR and immersive tech.
Cross-Reality Integration
One of the most exciting shifts is the move toward cross-reality (XR) integration. This involves combining elements from virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) into unified, flexible experiences. Users will move effortlessly between realities, attending a VR meeting, using AR for navigation, and reviewing 3D models in MR, all in a single workflow.
This kind of interoperability is already underway. Platforms are becoming more flexible, and hardware is evolving to support multiple modes. In this context, cloud-powered solutions like Vagon Streams will play a key role by enabling users to switch between high-performance applications without needing local upgrades.
Looking to expand your VR or MR workflow without a high-end machine? Check out Vagon Streams Pricing to see how you can access the best VR tools on demand, no heavy desktop setup required.
Advancements in 3D Capture and Representation
Creating lifelike virtual environments depends on how we capture and recreate the real world. In 2025, new 3D capture technologies, such as photogrammetry and Gaussian splatting, are raising the bar for realism. These methods allow users to scan real objects or spaces and convert them into high-resolution 3D assets.
This has massive potential for industries like real estate, game development, and cultural preservation. With a product roadmap software that integrates immersive tools, teams can embed these virtual experiences directly into their planning by mapping AR and VR sessions, linking use case prototypes to roadmap initiatives, and tracking progress in a unified visual timeline.
As scanning tools become more affordable and AI improves the reconstruction process, creators of all sizes will be able to build photorealistic content with ease.

A New Phase of Reality
Virtual reality is not a separate world anymore, it’s becoming part of our reality. With AI-generated content, spatial interaction, and real-world data streaming into immersive environments, we’re moving toward a phase where digital and physical experiences are tightly connected.
For users, this means more control and creativity. For businesses, it means entirely new markets and workflows. For developers, it’s a challenge, and an invitation to build what comes next.
And with cloud-native platforms like Vagon Streams reducing the technical barriers, more people will be able to participate in building, using, and shaping that future.
Final Thoughts & Conclusion
In 2025, virtual reality is no longer limited to experimental use or niche gaming. It’s a powerful tool integrated into how we train teams, visualize ideas, and deliver interactive experiences. As VR intersects with AI, spatial computing, and cloud infrastructure, the focus is shifting from standalone systems to seamless, scalable ecosystems.
This shift brings new technical demands: smooth performance, low-latency delivery, and real-time access to high-fidelity content, regardless of device. Vagon Streams addresses these challenges with a cloud-native pixel streaming platform designed for delivering VR and 3D applications without requiring local high-end hardware.
Backed by NVIDIA RTX GPU infrastructure and distributed across more than 20 global data centers, Vagon Streams ensures responsive and visually rich experiences from nearly any location. It supports industry-standard tools like Unreal Engine 5 Pixel Streaming and Unity Render Streaming, making it ideal for developers, studios, and enterprise teams working with complex or interactive 3D content.
With no-code setup, white-label customization, and built-in analytics, teams can deploy branded immersive experiences and track performance without building infrastructure from scratch. Flexible usage controls also help manage costs while scaling to meet varying project demands.
As VR becomes more embedded in real-world workflows, platforms like Vagon Streams are enabling the next generation of interactive content creation and delivery—remotely, efficiently, and at scale.
To get started or learn more, visit Vagon Streams.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What advancements have been made in VR hardware in 2025?
In 2025, VR headsets are becoming lighter, more comfortable, and offer higher resolution displays. Devices like Meta Quest 3 and Apple Vision Pro feature better depth tracking, micro-OLED screens, and inside-out tracking systems. There's also a push toward affordability and accessibility, allowing entry-level headsets to deliver strong performance at lower prices. Additionally, lightweight smart glasses and XR wearables are emerging, allowing users to interact with digital content while staying connected to the physical world.
2. How is AI integrated into VR experiences in 2025?
AI is enhancing VR by personalizing content and improving user interactions. Machine learning algorithms adapt virtual environments to individual users, adjusting difficulty levels in training or games. AI-driven avatars and NPCs are becoming more lifelike, understanding natural language and responding in realistic ways. Generative AI is also changing how VR content is created, allowing developers to generate 3D assets or entire environments quickly, speeding up production and reducing the need for manual modeling.
3. What industries are benefiting from VR in 2025?
VR is being used in industries like healthcare, education, retail, manufacturing, and more. In healthcare, VR aids in training and surgery simulations. In education, students can explore historical sites or complex scientific concepts virtually. Retailers and manufacturers use VR for training, prototyping, and remote collaboration. Cloud streaming platforms like Vagon Streams are making it easier for businesses to access these tools without needing high-end local hardware.
4. How is VR changing social interaction and entertainment?
Beyond gaming, VR is revolutionizing how people connect socially. Platforms like VRChat and Horizon Worlds allow users to meet, collaborate, or just socialize in immersive virtual environments. VR is also being used for immersive storytelling, where users are part of the narrative. Interactive films and 360° documentaries are offering new ways for creators to engage audiences, while cloud streaming makes these experiences more accessible, even on lower-end devices.
5. What is mixed reality (MR), and how is it different from VR?
Mixed reality (MR) blends real-world and virtual elements into a single, interactive space. Unlike VR, which immerses you fully in a virtual environment, MR allows you to interact with digital content while remaining aware of your physical surroundings. Devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Microsoft HoloLens 2 are leading MR advancements, allowing users to manipulate 3D models or control digital content in real time. MR is used in design, education, and industrial applications, offering a more seamless integration of physical and digital worlds.
6. How does cloud streaming impact VR and MR experiences?
Cloud streaming platforms like Vagon Streams are removing the need for high-performance local hardware. By offloading intensive computing to the cloud, users can access VR and MR applications from lightweight devices, such as older laptops or standalone headsets. This accessibility expands VR and MR use cases, allowing professionals, creators, and learners to tap into powerful immersive tools without needing high-end setups.
7. What role does AI play in making VR content creation faster and more efficient?
AI-powered tools enable faster creation of VR environments and assets. With generative AI, developers can describe a scene, and AI will generate 3D models or animations based on those descriptions. This speeds up the content creation process and allows smaller teams or independent creators to produce high-quality VR content. AI is also making it easier to personalize content for users, adjusting environments and experiences in real time.
8. What are the emerging trends in VR beyond 2025?
In the future, cross-reality (XR) integration will allow users to move between VR, AR, and MR seamlessly. Advancements in 3D capture technologies will lead to more lifelike virtual environments, enabling industries like real estate, game development, and cultural preservation to create photorealistic VR experiences. Additionally, ethics and privacy concerns will become more important as VR platforms handle sensitive user data, raising questions about data collection, user safety, and the design of virtual environments.
9. Can VR be used for professional and enterprise purposes?
Yes, VR is being increasingly adopted by enterprises for training, product design, and collaboration. Companies in fields like healthcare, aviation, and retail are using VR for simulations and employee training. VR also enables collaboration among teams spread across the globe, allowing them to work together in virtual spaces to review 3D models and make decisions in real time. Platforms like Vagon Streams are making these immersive tools accessible to a broader audience, without the need for expensive local setups.
10. How can creators and developers take advantage of VR in 2025?
Creators can leverage advancements in VR hardware, AI, and cloud streaming to produce high-quality, immersive content more efficiently. AI tools can help streamline the creation process, while cloud platforms like Vagon Streams offer access to high-performance VR tools on demand. As VR continues to evolve, developers will have new opportunities to create adaptive, intelligent environments that provide personalized experiences for users.
Virtual Reality (VR) has rapidly evolved from niche gaming tech into a mainstream tool reshaping industries in 2025. Thanks to lighter headsets, sharper displays, and more affordable pricing, VR is now used for far more than entertainment.
Today, architects walk through virtual buildings before construction begins. Students explore historical sites in digital classrooms. Remote teams collaborate in virtual offices, while doctors practice surgeries in immersive simulations. VR has become a platform for real-world problem-solving, not just play.
This transformation is driven not only by hardware but also by new technologies like generative AI, spatial computing, and cloud VR streaming. Platforms such as Vagon Streams now allow users to access powerful VR applications directly from the cloud, removing the need for expensive PCs or bulky equipment.
As VR adoption grows, expectations around user experience, accessibility, and content performance are also shifting. In this post, we’ll explore the key VR trends in 2025 that are shaping the future of immersive tech — and how creators, educators, and professionals can benefit.
#1. Hardware Innovations and Accessibility
The growth of virtual reality in 2025 is tightly linked to the evolution of VR hardware. Devices are not only getting more powerful, but also more accessible, comfortable, and affordable. These changes are crucial for bringing immersive experiences to a wider audience.
Lighter, Sharper, Smarter Headsets
In recent years, VR headsets have made a significant leap in performance and design. Devices like the Meta Quest 3 and Apple Vision Pro have raised the bar with higher-resolution displays, better depth tracking, and streamlined form factors. Advanced lenses, micro-OLED screens, and inside-out tracking systems have become the new standard, offering sharper visuals without the bulk.
Comfort has also become a focus. Manufacturers are prioritizing weight distribution, airflow, and adjustable fittings, making it easier to spend extended time in VR without fatigue. Battery life and wireless connectivity have improved as well, giving users more freedom to move.
These improvements are especially important for industries using VR in training, education, or design, places where long sessions and high precision are the norm.

Affordability Expands the Market
VR is becoming more accessible not just in form, but in cost. As production scales and competition grows, entry-level headsets with solid performance are now available at prices once unthinkable. This shift is opening up VR to students, independent creators, and small businesses.
At the same time, cloud-powered streaming platforms like Vagon Streams are removing the need for high-end local hardware altogether. By offloading the compute load to the cloud, users can run intensive VR applications from lightweight devices, even older laptops or standalone headsets.
Smart Glasses and Wearables
While full VR headsets are advancing, lightweight alternatives are emerging fast. Smart glasses and XR (extended reality) wearables now bridge the gap between virtual and real. Devices like Meta’s Ray-Ban Stories or Google’s Project Astra blend audio, visual cues, and spatial awareness into sleek, glasses-style hardware.
These wearables allow users to interact with digital content without losing connection to their physical environment. For everyday tasks, remote assistance, or hybrid collaboration, they offer a compelling mix of utility and minimalism.

The Bottom Line
In 2025, hardware is no longer a barrier for most VR users. Whether through affordable headsets, sleek smart glasses, or cloud streaming, accessing immersive content is easier than ever. This broader reach is helping VR expand into new industries and use cases, and setting the stage for the next wave of innovation.
As VR hardware continues to advance, creators are seeing a whole new world of possibilities. If you're diving into VR development, it's essential to understand how software like Blender for Virtual Reality can enhance your creations.
#2. AI Integration Enhancing VR Experiences
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the most powerful forces accelerating VR’s evolution in 2025. As VR environments grow more complex and personalized, AI is playing a key role in shaping how users interact with virtual worlds, and how those worlds are created.
Personalized Content and Smarter Interactions
One of the most visible impacts of AI in VR is personalization. Machine learning algorithms now adapt virtual environments to individual users in real time. Whether it’s adjusting the difficulty level in a VR training session, modifying a learning path in an educational simulation, or fine-tuning narrative pacing in a VR game, AI makes the experience feel more tailored and responsive.
AI-driven avatars are also becoming more lifelike. Voice synthesis and natural language processing allow NPCs (non-player characters) and virtual assistants to understand and respond to users with realistic tone and behavior, creating smoother, more engaging interactions.
This is especially important in education, therapy, and collaborative platforms, where feeling “understood” by the system boosts effectiveness and comfort.

Generative AI and Dynamic Worldbuilding
AI isn’t just improving how we use VR, it’s also changing how VR content is built. With the rise of generative AI, creators can design environments, objects, and entire scenarios faster than ever.
Instead of manually modeling every element, developers can now describe a scene in simple terms and let AI generate 3D assets or animations. This speeds up production and makes worldbuilding more accessible to smaller teams and independent creators.
Some platforms even use AI to generate environments on-the-fly during gameplay or interaction, allowing for adaptive storytelling and unique user journeys.
Smarter Hardware and Wearables
AI also powers the next generation of smart wearables. For instance, Meta’s Ray-Ban smart glasses now include AI capabilities that allow users to ask questions about what they see in real time, essentially turning their view into an interactive experience.
On a broader level, these AI features help streamline user interfaces. Instead of relying on complex menus or manual controls, users can interact with VR systems through natural language, gestures, or even gaze tracking, all interpreted by intelligent algorithms.

Why It Matters
AI and VR are converging fast, creating immersive environments that feel intelligent, adaptive, and uniquely personal. For creators, this means faster content production and smarter tools. For users, it means more engaging and seamless experiences.
And when paired with cloud infrastructure, like Vagon Streams, AI-powered VR doesn’t have to be limited by local computing power. Heavy processing can happen in the cloud, with results streamed directly to your device, making high-performance AI in VR accessible to more people.
With AI’s growing role in VR, we’re entering a phase of smarter, more adaptive virtual environments. To create realistic AI-driven content, developers should explore tools and resources in the VR space, such as those discussed in our article on top graphics cards for VR, which are key for achieving higher-quality AI interactions in virtual worlds.
#3. Enterprise and Industrial Applications
Virtual reality is no longer confined to entertainment or niche research labs. In 2025, VR is firmly established as a serious tool across enterprise sectors, from retail and manufacturing to healthcare and education. VR is also transforming retail logistics—when combined with advanced 3PL WMS solutions, it enables virtual walkthroughs and real-time training that help optimize inventory handling and streamline supply chain operations.
VR for Training and Simulation
One of the strongest use cases for VR in industry is workforce training. Simulations in VR offer a safe, repeatable, and measurable environment for employees to learn and practice skills. Sectors like retail, aviation, energy, and emergency response now use VR to prepare staff for real-world scenarios without real-world risks.
Walmart, for example, uses VR to train employees on customer service, holiday rush prep, and emergency protocols. In healthcare, hospitals simulate surgeries or high-stress environments to prepare medical staff without involving real patients.
These training programs are not only safer, they’re also more scalable. With cloud-based platforms like Vagon Streams, large teams can access the same immersive modules from different locations, without requiring expensive local setups.

Healthcare and Therapy
VR is making a growing impact in medicine as well. Surgeons use VR for pre-operative planning and fine-tuning procedures in 3D environments that mimic real anatomy. Therapists use VR exposure therapy to help patients with PTSD, anxiety, or phobias by gradually introducing controlled stimuli in a safe setting. In parallel, healthcare wearable app development is enabling real-time monitoring and feedback, making these immersive treatments even more data-driven and personalized.
Additionally, VR is being used for rehabilitation, offering patients interactive exercises that help them regain mobility or cognitive function in a gamified, trackable format.
These applications rely on realism, responsiveness, and accessibility, traits made more viable when combined with AI and cloud infrastructure.

Prototyping, Design, and Collaboration
VR is also revolutionizing product development. Designers and engineers can build and test prototypes in virtual environments before committing to physical production. This is already in use by companies like BMW, which has created virtual factories using tools like NVIDIA’s Omniverse to simulate and optimize workflows before they go live.
Architects and construction teams walk through buildings in VR before a single brick is laid. Industrial designers iterate on product concepts more quickly using immersive modeling tools. And with VR collaboration spaces, teams spread across continents can meet inside the same virtual workspace, examine 3D models together, and make decisions in real time.
This ability to collaborate inside immersive environments is particularly powerful when paired with cloud streaming. Even team members with minimal hardware can join and contribute through platforms like Vagon Streams.

A Strategic Investment
For enterprises, VR is no longer a gamble, it’s a strategic investment. The technology reduces costs, increases safety, speeds up innovation cycles, and opens up new collaboration models. Cloud streaming platforms like Vagon Streams support this by lowering the technical entry barrier, making immersive work tools available on a broader range of devices.
As organizations continue to digitize workflows, VR is proving to be more than just a novelty. It’s a core part of the industrial and professional tech stack.
#4. Evolution of VR in Entertainment and Social Interaction
Entertainment helped virtual reality find its first audience, and in 2025, it’s still one of the most vibrant areas for innovation. But the definition of “VR entertainment” has evolved. It’s no longer just about games, it’s about social connection, shared experiences, and immersive storytelling that blurs the line between fiction and reality.
Next-Generation VR Gaming
Gaming continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in VR. Today’s titles offer expansive, interactive worlds, sophisticated physics, and multiplayer modes that make players feel truly present. Haptic feedback suits, motion tracking, and eye-tracking features are becoming more common, letting players feel resistance when they pull a bowstring or interact with objects in 3D space.
Developers are also leaning into procedural generation and adaptive AI to create dynamic, personalized game environments. This means no two sessions are exactly the same, and players are rewarded with deeper immersion and longer engagement.
As high-fidelity gaming becomes more compute-intensive, cloud streaming is playing a bigger role. Platforms like Vagon Streams let users run demanding VR games without needing a gaming PC, just a stable connection and a lightweight headset.

Immersive Storytelling
Filmmakers and artists are also turning to VR to tell stories in new ways. Unlike traditional cinema, VR places the viewer inside the narrative. You’re not watching from a distance, you’re surrounded by the story.
Interactive films, 360° documentaries, and virtual theater are gaining traction, offering creators a new palette of tools. Audiences, in turn, enjoy richer and more emotionally resonant experiences.
As creators experiment with these formats, cloud tools are once again reducing barriers. With heavy rendering handled remotely, artists can focus on creative direction, even on modest devices.
Virtual Social Worlds
Beyond games, VR is changing how we socialize. Platforms like VRChat, Horizon Worlds, and Rec Room have become digital gathering spaces where people meet, collaborate, and even perform together in real time. Users attend concerts, host workshops, or just hang out in shared 3D spaces, with a growing focus on self-expression through customizable avatars and environments.
These spaces are becoming more important in an era of hybrid and remote living. VR makes distance feel smaller, offering a level of presence that traditional video calls can’t match.
Still, developers are working to improve accessibility, moderation tools, and user safety. These social environments need clear guidelines and thoughtful design to ensure they remain inclusive and healthy spaces.

A More Connected Future
Entertainment and social interaction are driving mainstream adoption of VR. But they’re also pushing the medium forward, introducing more expressive tools, deeper engagement, and more human experiences. With hardware improving and cloud platforms making VR more accessible, 2025 is a turning point in how we connect, create, and escape together.
For creators looking to take their VR gaming or interactive experiences to the next level, understanding the tools and platforms available is crucial. Check out our tips for creating VR in Unreal Engine to help bring your VR visions to life.
#5. Emergence of Mixed Reality and Spatial Computing
In 2025, the lines between physical and virtual spaces are becoming increasingly blurred. Thanks to major strides in mixed reality (MR) and spatial computing, users are no longer just inside virtual environments, they’re interacting with digital content layered directly onto their physical world. This convergence is unlocking new possibilities in productivity, design, education, and everyday life.
What is Mixed Reality?
Mixed reality sits between traditional VR and augmented reality (AR). It merges real-world and digital elements into a single, interactive space. Unlike VR, which fully immerses you in a virtual environment, MR allows digital content to respond to the physical world in real time.
Devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Microsoft HoloLens 2 are leading the charge. These headsets can place a 3D model on your actual desk or let you manipulate digital controls floating in your living room. The key is spatial awareness, these systems understand the geometry of your environment and adapt virtual content accordingly.

Rise of Spatial Computing
Spatial computing takes this further. It refers to the ability of machines to understand and respond to the physical world using sensors, cameras, and AI. Spatial computing powers gesture recognition, room-scale mapping, and eye-tracking, turning your environment into an interface.
This means users can walk around a digital object, resize it with their hands, or glance at a control panel to activate it. Architects can review building models inside the construction site. Teachers can turn a classroom into a living solar system. Product teams can brainstorm using virtual whiteboards in shared space, without being in the same location.
These experiences are no longer just futuristic demos. They’re being deployed in real workflows across education, industrial design, and healthcare.
Making MR More Accessible
Historically, MR and spatial computing required powerful hardware and dedicated environments. But with cloud streaming, that’s changing fast. Complex spatial applications can now run remotely and be delivered to lightweight headsets or even tablets.
For example, with Vagon Streams, professionals can access MR design tools or spatial simulations from wherever they are, no need for a high-end local machine. This flexibility expands the reach of mixed reality beyond enterprise labs into classrooms, studios, and homes.

A Shift in How We Work and Learn
The biggest impact of MR and spatial computing is how it transforms interaction. Instead of using a mouse or touchpad, people are using movement, space, and presence to engage with digital content. This makes technology more intuitive, and potentially more inclusive.
As spatial computing becomes more integrated into daily workflows, we’ll see a shift toward environments that feel more human and immersive. And with cloud infrastructure reducing the technical barriers, we’re entering an era where physical and digital aren’t separate, they’re merged.

#6. Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
As we look beyond 2025, virtual reality continues to evolve in ways that extend far beyond headsets and entertainment. The next wave of innovation is about deeper integration, smarter systems, and a more seamless blend between the physical and digital worlds. Here are some of the key trends shaping the future of VR and immersive tech.
Cross-Reality Integration
One of the most exciting shifts is the move toward cross-reality (XR) integration. This involves combining elements from virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) into unified, flexible experiences. Users will move effortlessly between realities, attending a VR meeting, using AR for navigation, and reviewing 3D models in MR, all in a single workflow.
This kind of interoperability is already underway. Platforms are becoming more flexible, and hardware is evolving to support multiple modes. In this context, cloud-powered solutions like Vagon Streams will play a key role by enabling users to switch between high-performance applications without needing local upgrades.
Looking to expand your VR or MR workflow without a high-end machine? Check out Vagon Streams Pricing to see how you can access the best VR tools on demand, no heavy desktop setup required.
Advancements in 3D Capture and Representation
Creating lifelike virtual environments depends on how we capture and recreate the real world. In 2025, new 3D capture technologies, such as photogrammetry and Gaussian splatting, are raising the bar for realism. These methods allow users to scan real objects or spaces and convert them into high-resolution 3D assets.
This has massive potential for industries like real estate, game development, and cultural preservation. With a product roadmap software that integrates immersive tools, teams can embed these virtual experiences directly into their planning by mapping AR and VR sessions, linking use case prototypes to roadmap initiatives, and tracking progress in a unified visual timeline.
As scanning tools become more affordable and AI improves the reconstruction process, creators of all sizes will be able to build photorealistic content with ease.

A New Phase of Reality
Virtual reality is not a separate world anymore, it’s becoming part of our reality. With AI-generated content, spatial interaction, and real-world data streaming into immersive environments, we’re moving toward a phase where digital and physical experiences are tightly connected.
For users, this means more control and creativity. For businesses, it means entirely new markets and workflows. For developers, it’s a challenge, and an invitation to build what comes next.
And with cloud-native platforms like Vagon Streams reducing the technical barriers, more people will be able to participate in building, using, and shaping that future.
Final Thoughts & Conclusion
In 2025, virtual reality is no longer limited to experimental use or niche gaming. It’s a powerful tool integrated into how we train teams, visualize ideas, and deliver interactive experiences. As VR intersects with AI, spatial computing, and cloud infrastructure, the focus is shifting from standalone systems to seamless, scalable ecosystems.
This shift brings new technical demands: smooth performance, low-latency delivery, and real-time access to high-fidelity content, regardless of device. Vagon Streams addresses these challenges with a cloud-native pixel streaming platform designed for delivering VR and 3D applications without requiring local high-end hardware.
Backed by NVIDIA RTX GPU infrastructure and distributed across more than 20 global data centers, Vagon Streams ensures responsive and visually rich experiences from nearly any location. It supports industry-standard tools like Unreal Engine 5 Pixel Streaming and Unity Render Streaming, making it ideal for developers, studios, and enterprise teams working with complex or interactive 3D content.
With no-code setup, white-label customization, and built-in analytics, teams can deploy branded immersive experiences and track performance without building infrastructure from scratch. Flexible usage controls also help manage costs while scaling to meet varying project demands.
As VR becomes more embedded in real-world workflows, platforms like Vagon Streams are enabling the next generation of interactive content creation and delivery—remotely, efficiently, and at scale.
To get started or learn more, visit Vagon Streams.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What advancements have been made in VR hardware in 2025?
In 2025, VR headsets are becoming lighter, more comfortable, and offer higher resolution displays. Devices like Meta Quest 3 and Apple Vision Pro feature better depth tracking, micro-OLED screens, and inside-out tracking systems. There's also a push toward affordability and accessibility, allowing entry-level headsets to deliver strong performance at lower prices. Additionally, lightweight smart glasses and XR wearables are emerging, allowing users to interact with digital content while staying connected to the physical world.
2. How is AI integrated into VR experiences in 2025?
AI is enhancing VR by personalizing content and improving user interactions. Machine learning algorithms adapt virtual environments to individual users, adjusting difficulty levels in training or games. AI-driven avatars and NPCs are becoming more lifelike, understanding natural language and responding in realistic ways. Generative AI is also changing how VR content is created, allowing developers to generate 3D assets or entire environments quickly, speeding up production and reducing the need for manual modeling.
3. What industries are benefiting from VR in 2025?
VR is being used in industries like healthcare, education, retail, manufacturing, and more. In healthcare, VR aids in training and surgery simulations. In education, students can explore historical sites or complex scientific concepts virtually. Retailers and manufacturers use VR for training, prototyping, and remote collaboration. Cloud streaming platforms like Vagon Streams are making it easier for businesses to access these tools without needing high-end local hardware.
4. How is VR changing social interaction and entertainment?
Beyond gaming, VR is revolutionizing how people connect socially. Platforms like VRChat and Horizon Worlds allow users to meet, collaborate, or just socialize in immersive virtual environments. VR is also being used for immersive storytelling, where users are part of the narrative. Interactive films and 360° documentaries are offering new ways for creators to engage audiences, while cloud streaming makes these experiences more accessible, even on lower-end devices.
5. What is mixed reality (MR), and how is it different from VR?
Mixed reality (MR) blends real-world and virtual elements into a single, interactive space. Unlike VR, which immerses you fully in a virtual environment, MR allows you to interact with digital content while remaining aware of your physical surroundings. Devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Microsoft HoloLens 2 are leading MR advancements, allowing users to manipulate 3D models or control digital content in real time. MR is used in design, education, and industrial applications, offering a more seamless integration of physical and digital worlds.
6. How does cloud streaming impact VR and MR experiences?
Cloud streaming platforms like Vagon Streams are removing the need for high-performance local hardware. By offloading intensive computing to the cloud, users can access VR and MR applications from lightweight devices, such as older laptops or standalone headsets. This accessibility expands VR and MR use cases, allowing professionals, creators, and learners to tap into powerful immersive tools without needing high-end setups.
7. What role does AI play in making VR content creation faster and more efficient?
AI-powered tools enable faster creation of VR environments and assets. With generative AI, developers can describe a scene, and AI will generate 3D models or animations based on those descriptions. This speeds up the content creation process and allows smaller teams or independent creators to produce high-quality VR content. AI is also making it easier to personalize content for users, adjusting environments and experiences in real time.
8. What are the emerging trends in VR beyond 2025?
In the future, cross-reality (XR) integration will allow users to move between VR, AR, and MR seamlessly. Advancements in 3D capture technologies will lead to more lifelike virtual environments, enabling industries like real estate, game development, and cultural preservation to create photorealistic VR experiences. Additionally, ethics and privacy concerns will become more important as VR platforms handle sensitive user data, raising questions about data collection, user safety, and the design of virtual environments.
9. Can VR be used for professional and enterprise purposes?
Yes, VR is being increasingly adopted by enterprises for training, product design, and collaboration. Companies in fields like healthcare, aviation, and retail are using VR for simulations and employee training. VR also enables collaboration among teams spread across the globe, allowing them to work together in virtual spaces to review 3D models and make decisions in real time. Platforms like Vagon Streams are making these immersive tools accessible to a broader audience, without the need for expensive local setups.
10. How can creators and developers take advantage of VR in 2025?
Creators can leverage advancements in VR hardware, AI, and cloud streaming to produce high-quality, immersive content more efficiently. AI tools can help streamline the creation process, while cloud platforms like Vagon Streams offer access to high-performance VR tools on demand. As VR continues to evolve, developers will have new opportunities to create adaptive, intelligent environments that provide personalized experiences for users.
Scalable Pixel and Application Streaming
Run your Unity or Unreal Engine application on any device, share with your clients in minutes, with no coding.

Scalable Pixel and Application Streaming
Run your Unity or Unreal Engine application on any device, share with your clients in minutes, with no coding.


Ready to focus on your creativity?
Vagon gives you the ability to create & render projects, collaborate, and stream applications with the power of the best hardware.

Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
The Best AI Video Generators in 2026: Tested Tools, Real Results
The Best AI Photo Editors in 2026: Tools, Workflows, and Real Results
How to Improve Unity Game Performance
How to Create Video Proxies in Premiere Pro to Edit Faster
Top SketchUp Alternatives for 3D Modeling in 2026
How to Stop Premiere Pro from Crashing in 2026
Best PC for Blender in 2026 That Makes Blender Feel Fast
Best Laptops for Digital Art and Artists in 2026 Guide
How to Use the 3D Cursor in Blender
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
The Best AI Video Generators in 2026: Tested Tools, Real Results
The Best AI Photo Editors in 2026: Tools, Workflows, and Real Results
How to Improve Unity Game Performance
How to Create Video Proxies in Premiere Pro to Edit Faster
Top SketchUp Alternatives for 3D Modeling in 2026
How to Stop Premiere Pro from Crashing in 2026
Best PC for Blender in 2026 That Makes Blender Feel Fast
Best Laptops for Digital Art and Artists in 2026 Guide
How to Use the 3D Cursor in Blender
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
The Best AI Video Generators in 2026: Tested Tools, Real Results
The Best AI Photo Editors in 2026: Tools, Workflows, and Real Results
How to Improve Unity Game Performance
How to Create Video Proxies in Premiere Pro to Edit Faster
Top SketchUp Alternatives for 3D Modeling in 2026
How to Stop Premiere Pro from Crashing in 2026
Best PC for Blender in 2026 That Makes Blender Feel Fast
Best Laptops for Digital Art and Artists in 2026 Guide
How to Use the 3D Cursor in Blender
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog


