Instant Connection for Pixel Streaming
— New Feature Automated Setup

AutoCAD vs Autodesk Inventor: Which Is Best For Your Workflow?
AutoCAD vs Autodesk Inventor: Which Is Best For Your Workflow?
AutoCAD vs Autodesk Inventor: Which Is Best For Your Workflow?
Published on September 10, 2024
Table of Contents
Choosing the right CAD software can make or break a project. Whether you're designing skyscrapers or simulating mechanical systems, the right tool saves time and boosts productivity. Two industry titans often stand out: AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor. But which is the best fit for your needs? This guide dives into the core differences between these two powerful platforms—breaking down features, ease of use, industry applications, and more. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of which tool is right for your next project.
Quick Overview of AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor
Both AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor are flagship products from Autodesk, each catering to different design needs. AutoCAD is renowned for its flexibility in 2D and 3D design across various industries, from architecture to engineering. On the other hand, Autodesk Inventor focuses on mechanical design, specializing in complex 3D assemblies and simulations.
While AutoCAD offers versatility for architectural plans, drafting, and civil engineering, Inventor is built for those tackling mechanical products, offering parametric modeling, design automation, and simulation capabilities. If you’re unsure which tool is best, understanding their key strengths will help you make the right choice.
What is AutoCAD?
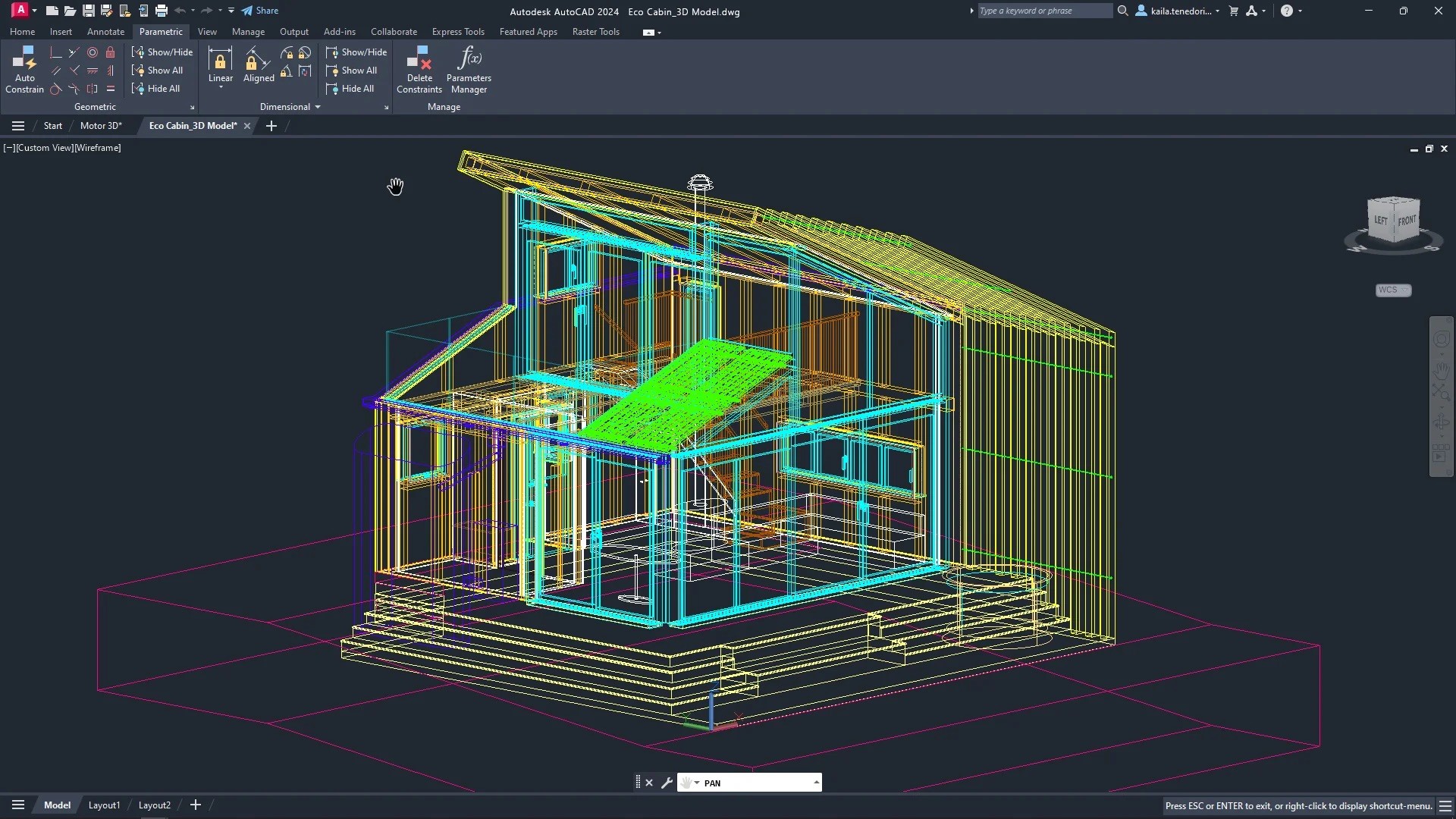
AutoCAD in a Nutshell:
AutoCAD is an industry-standard for 2D and 3D design. It’s widely used in architecture, civil engineering, and drafting, allowing professionals to create precise, detailed designs. AutoCAD's strength lies in its versatility—it can handle everything from floor plans to intricate 3D models. If AutoCAD doesn't meet all your needs, exploring some of the top alternatives to AutoCAD could provide valuable options for your specific workflow.
You might also find it useful to explore how AutoCAD compares to Blender if you're considering more creative or open-source 3D modeling alternatives.
"AutoCAD is your go-to tool for precise, detailed 2D drawings."
Whether you’re drafting architectural blueprints or creating technical schematics, AutoCAD’s flexibility ensures you have the right tool for the job.
You can also check out our GPU Guide for tips to use GPU, along with speed up and acceleration tips for Autodesk AutoCAD.
What is Autodesk Inventor?
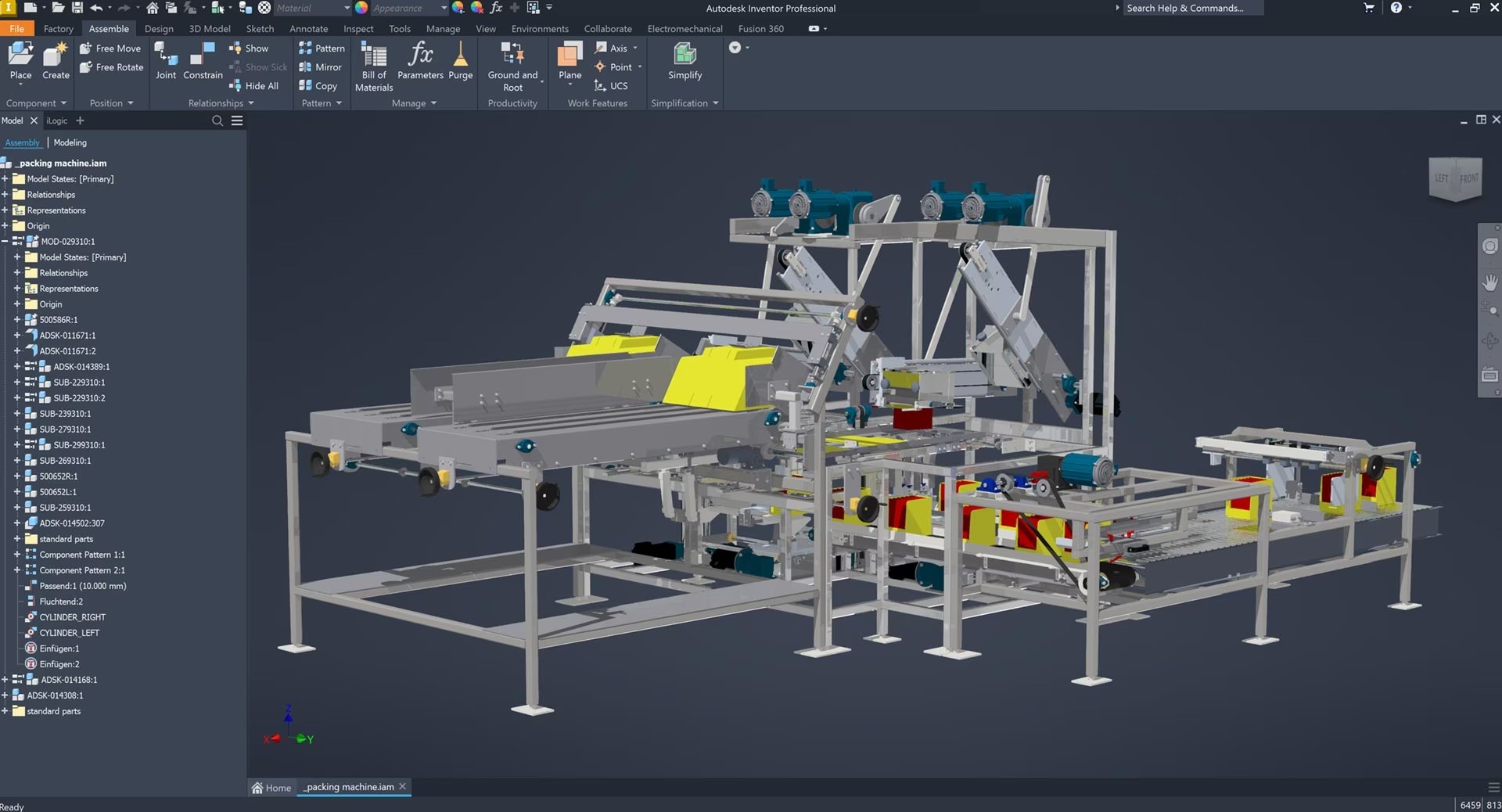
Autodesk Inventor in a Nutshell:
Autodesk Inventor is specifically designed for mechanical design and 3D CAD modeling. It excels in product design, complex assemblies, and simulation tasks. The software's parametric design capabilities allow you to tweak any element of your design easily, making it perfect for engineers working on intricate mechanical systems.
"If you're designing complex mechanical systems, Inventor is built for you."
With built-in tools for testing designs, simulating motion, and running stress analyses, Inventor streamlines the mechanical design process from concept to production.
Key Differences Between AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor
When deciding between AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor, understanding their unique strengths is key. These software solutions may come from the same family, but they cater to different needs, workflows, and industries. From the core focus on 2D vs. 3D design to specialized toolsets, each platform offers distinct advantages depending on your project type. Let’s break down the primary differences that will help you choose the right tool for the job.
2D vs 3D Design
AutoCAD: If you’re working heavily with 2D drawings, AutoCAD is the best fit. It's renowned for precision in creating floor plans, technical blueprints, and other detailed 2D drafts. While AutoCAD does offer some 3D capabilities, its real power shines in the creation of intricate 2D schematics. Think architectural layouts, civil engineering plans, and more. If you're comparing other CAD software, you might also be interested in this detailed guide on AutoCAD vs SolidWorks to further refine your decision.
Autodesk Inventor: Inventor is all about 3D parametric modeling. If your focus is designing complex mechanical assemblies or prototypes, Inventor’s tools are built to handle it. With Inventor, you can design in 3D from the ground up, making it ideal for developing product components, testing assemblies, and running simulations to validate designs.
Industry Focus
AutoCAD: AutoCAD has cemented its role as the go-to software for architecture, civil engineering, and even some manufacturing processes. It's used to create detailed plans, technical drawings, and even infrastructure layouts, making it a versatile tool for a range of industries that need precise 2D documentation or light 3D visualizations.
Autodesk Inventor: When it comes to mechanical engineering, product design, and prototyping, Inventor takes the lead. The software is designed with manufacturers and engineers in mind, offering tools that help build and test mechanical systems before they ever go into production.
Features and Tools
AutoCAD: AutoCAD excels with its extensive 2D drafting tools, enabling users to create detailed technical drawings with ease. While it does provide some 3D modeling features, they aren’t its primary focus. AutoCAD is more about versatility—used across industries that rely on 2D plans, such as construction, architecture, and urban planning. If you're just getting started with AutoCAD, checking out some of the best AutoCAD courses can help you master its features faster.
Autodesk Inventor: Inventor is built for 3D parametric design, offering advanced tools for creating complex models and assemblies. It also goes beyond just design with its simulation tools, like stress analysis and motion studies. If you need to test how mechanical parts fit and interact before manufacturing, Inventor’s robust capabilities make it the preferred option.
User Interface & Ease of Use
The user interface of any software can greatly impact your efficiency, especially when working on complex designs. Both AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor offer customizable interfaces tailored to their respective uses, but each caters to different types of users. Here’s a look at how their interfaces stack up and what to expect in terms of ease of use.
AutoCAD
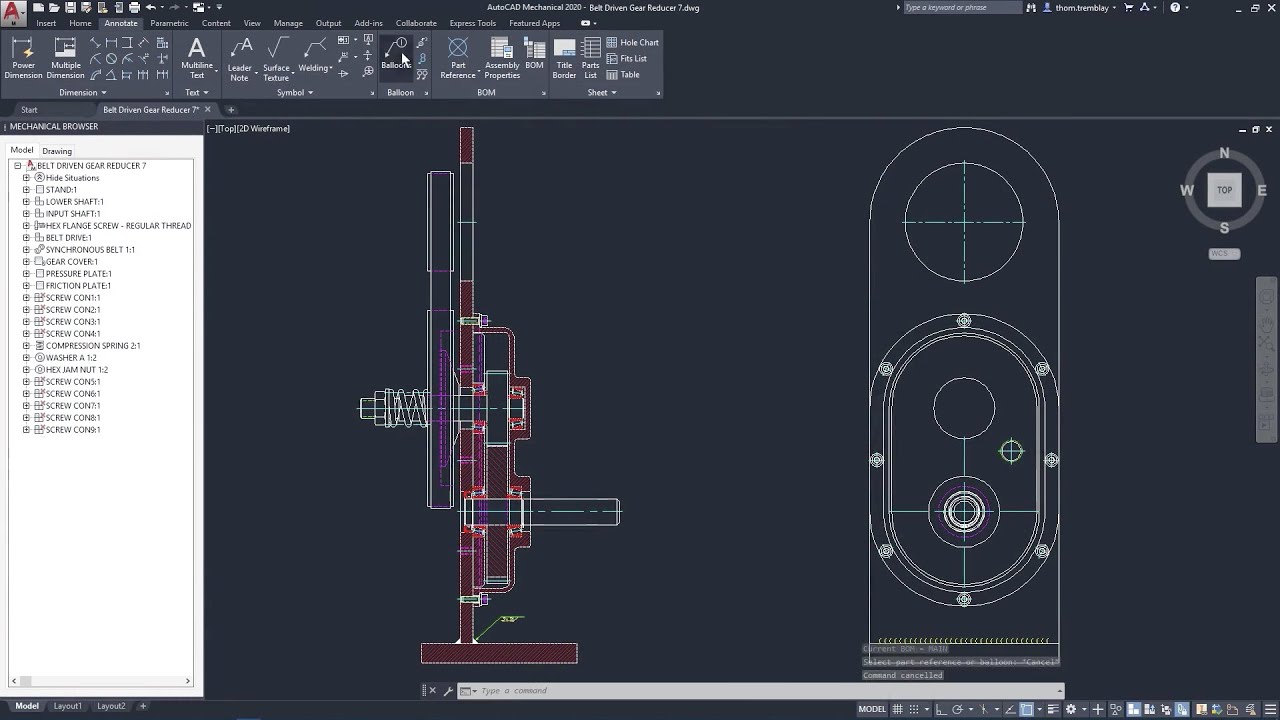
Simplicity: AutoCAD’s interface is known for its clean and intuitive layout, especially when it comes to 2D drafting. It’s designed to minimize distractions, so users can focus on creating precise drawings. The interface is straightforward, with easily accessible toolbars and a workspace that prioritizes clarity.
Learning Curve: AutoCAD’s learning curve is relatively gentle, particularly for those working on 2D designs. Beginners can quickly grasp the fundamentals, making it a great choice for new drafters, architects, and designers who need to get up to speed fast.
Customization: AutoCAD’s interface can be highly customized to fit individual workflows. You can arrange tool palettes, create custom commands, and even personalize shortcuts, enabling a tailored user experience that boosts productivity.
Autodesk Inventor
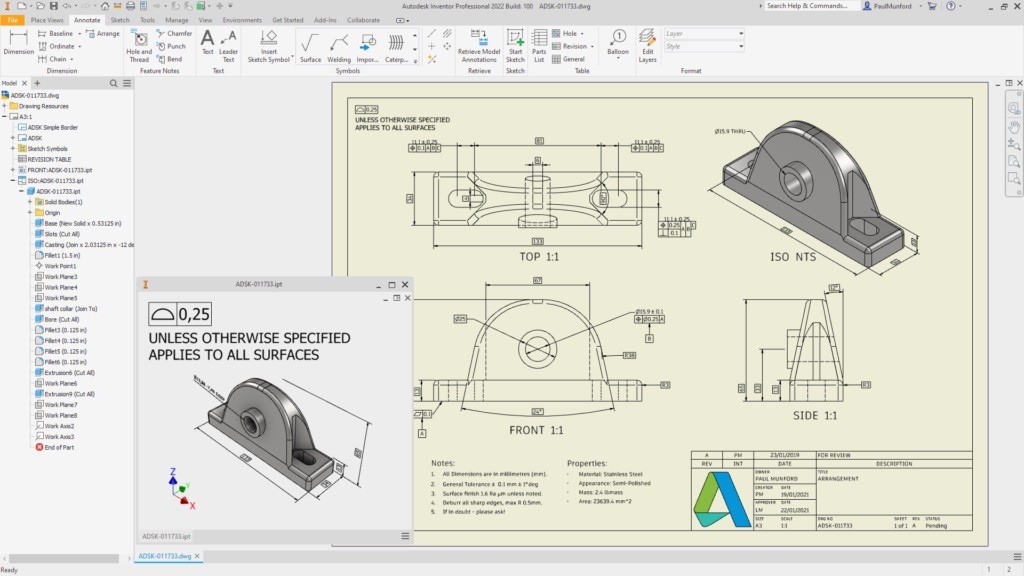
Complexity: In contrast, Autodesk Inventor comes with a feature-rich interface that offers a wide range of tools for 3D modeling, simulation, and assembly. The interface is more detailed, reflecting the complex projects it’s built for, but this can be overwhelming for new users at first.
Learning Curve: Due to its depth of features, Inventor has a steeper learning curve. However, mastering it pays off significantly as it opens the door to powerful 3D parametric modeling and simulation tools, perfect for engineers.
Best for Engineers: Inventor’s interface is specifically designed to meet the needs of engineers, making tasks like technical simulations and mechanical design both intuitive and efficient. If you’re looking to dive into the world of mechanical engineering, Inventor’s UI is crafted to support you.
Performance and File Compatibility
When it comes to performance and file handling, both AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor have distinct strengths, especially in how they manage resources and file formats.
AutoCAD: AutoCAD excels at handling DWG and DXF files, which are the industry standards for 2D drafting. Its lightweight nature means it doesn’t demand a lot from your system, making it ideal for users with moderate hardware setups. If you're using a lower-end device and don't have access to a high-powered GPU, there are ways to optimize AutoCAD’s performance. You can learn more about how to run AutoCAD on low-end devices without a GPU here. Additionally, AutoCAD integrates smoothly with other Autodesk products, ensuring seamless collaboration across different projects. For those looking to maximize efficiency, using AutoCAD on a cloud computer is a great way to work without high-end hardware constraints.
Autodesk Inventor: Inventor, on the other hand, works with more complex file types like IPT, IAM, and IDW, which are necessary for 3D models and mechanical assemblies. Given its advanced simulation and 3D rendering features, Inventor requires more robust computing power. It also supports various mechanical CAD formats such as STEP and IGES, making it highly compatible with industry-standard mechanical files, perfect for engineers and product designers.
Price Comparison
Pricing is another key factor when choosing between AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor. Both follow a subscription-based model, but the cost reflects their feature sets.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is generally more affordable, especially for professionals primarily needing 2D drafting tools. Its pricing is well-suited for architects, drafters, and engineers who don't require advanced 3D capabilities. If your focus is on floor plans, technical drawings, or simple 3D models, AutoCAD offers a cost-effective solution without sacrificing essential design features.
Autodesk Inventor
Autodesk Inventor comes with a higher price tag, but for good reason. Its robust 3D modeling, assembly, and simulation tools provide more advanced capabilities, justifying the cost for mechanical design professionals. While the upfront investment is higher, the return on investment (ROI) is significant for industries needing accurate simulations, stress analysis, and detailed mechanical designs.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor depends on your specific industry needs and design focus.
Choose AutoCAD If…
You work in architecture or civil engineering.
Your main focus is on precise 2D drafting and technical drawings.
You need an affordable, versatile tool that’s lightweight and widely used across industries.
Choose Autodesk Inventor If…
You’re in mechanical engineering, product design, or manufacturing.
You require advanced 3D parametric modeling and simulation capabilities.
You’re working on complex assemblies or prototypes that need precise testing and analysis.
Final Decision
AutoCAD shines in 2D drafting and versatility, making it a go-to for architects and drafters, while Autodesk Inventor is built for complex 3D mechanical design and simulations, catering to engineers and manufacturers. To find the best fit for your needs, assess your industry demands and project requirements. AutoCAD’s versatility has led to countless amazing designs—see some of the inspiring projects made with AutoCAD that demonstrate its capabilities.
Still unsure? With Vagon, you can test both AutoCAD and Inventor within seconds on cloud-powered computers, ensuring you get the best performance without needing high-end hardware. Once you’ve made your choice, you can also supercharge your workflow and renderings by leveraging Vagon’s cloud computing power—perfect for heavy projects and fast rendering times.
FAQs:
Is AutoCAD or Inventor better for beginners?
For beginners, AutoCAD is typically easier to start with, especially for those focusing on 2D drafting and technical drawings. Its interface is more intuitive for 2D work, while Inventor’s complexity may require more time to master, particularly for 3D modeling.
Can I use AutoCAD for 3D modeling?
Yes, AutoCAD does support 3D modeling, but it’s not as advanced as Inventor. AutoCAD is better suited for simpler 3D projects or visualizations, whereas Inventor specializes in complex 3D designs, assemblies, and simulations.
What industries benefit most from Inventor?
Autodesk Inventor is ideal for industries like mechanical engineering, product design, manufacturing, and aerospace, where creating and testing detailed 3D assemblies and prototypes is essential.
Which software has a steeper learning curve?
Inventor has a steeper learning curve due to its advanced 3D modeling and simulation tools. AutoCAD is more straightforward, particularly for those working in 2D environments.
Is AutoCAD cheaper than Inventor?
Yes, AutoCAD is generally more affordable than Inventor. It’s a good choice for professionals who don’t need advanced 3D capabilities or complex simulations.
Can AutoCAD and Inventor work together?
Absolutely! AutoCAD and Inventor are both Autodesk products, and their files can be easily integrated, making it simple to move between 2D designs in AutoCAD and more detailed 3D work in Inventor.
Choosing the right CAD software can make or break a project. Whether you're designing skyscrapers or simulating mechanical systems, the right tool saves time and boosts productivity. Two industry titans often stand out: AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor. But which is the best fit for your needs? This guide dives into the core differences between these two powerful platforms—breaking down features, ease of use, industry applications, and more. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of which tool is right for your next project.
Quick Overview of AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor
Both AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor are flagship products from Autodesk, each catering to different design needs. AutoCAD is renowned for its flexibility in 2D and 3D design across various industries, from architecture to engineering. On the other hand, Autodesk Inventor focuses on mechanical design, specializing in complex 3D assemblies and simulations.
While AutoCAD offers versatility for architectural plans, drafting, and civil engineering, Inventor is built for those tackling mechanical products, offering parametric modeling, design automation, and simulation capabilities. If you’re unsure which tool is best, understanding their key strengths will help you make the right choice.
What is AutoCAD?

AutoCAD in a Nutshell:
AutoCAD is an industry-standard for 2D and 3D design. It’s widely used in architecture, civil engineering, and drafting, allowing professionals to create precise, detailed designs. AutoCAD's strength lies in its versatility—it can handle everything from floor plans to intricate 3D models. If AutoCAD doesn't meet all your needs, exploring some of the top alternatives to AutoCAD could provide valuable options for your specific workflow.
You might also find it useful to explore how AutoCAD compares to Blender if you're considering more creative or open-source 3D modeling alternatives.
"AutoCAD is your go-to tool for precise, detailed 2D drawings."
Whether you’re drafting architectural blueprints or creating technical schematics, AutoCAD’s flexibility ensures you have the right tool for the job.
You can also check out our GPU Guide for tips to use GPU, along with speed up and acceleration tips for Autodesk AutoCAD.
What is Autodesk Inventor?

Autodesk Inventor in a Nutshell:
Autodesk Inventor is specifically designed for mechanical design and 3D CAD modeling. It excels in product design, complex assemblies, and simulation tasks. The software's parametric design capabilities allow you to tweak any element of your design easily, making it perfect for engineers working on intricate mechanical systems.
"If you're designing complex mechanical systems, Inventor is built for you."
With built-in tools for testing designs, simulating motion, and running stress analyses, Inventor streamlines the mechanical design process from concept to production.
Key Differences Between AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor
When deciding between AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor, understanding their unique strengths is key. These software solutions may come from the same family, but they cater to different needs, workflows, and industries. From the core focus on 2D vs. 3D design to specialized toolsets, each platform offers distinct advantages depending on your project type. Let’s break down the primary differences that will help you choose the right tool for the job.
2D vs 3D Design
AutoCAD: If you’re working heavily with 2D drawings, AutoCAD is the best fit. It's renowned for precision in creating floor plans, technical blueprints, and other detailed 2D drafts. While AutoCAD does offer some 3D capabilities, its real power shines in the creation of intricate 2D schematics. Think architectural layouts, civil engineering plans, and more. If you're comparing other CAD software, you might also be interested in this detailed guide on AutoCAD vs SolidWorks to further refine your decision.
Autodesk Inventor: Inventor is all about 3D parametric modeling. If your focus is designing complex mechanical assemblies or prototypes, Inventor’s tools are built to handle it. With Inventor, you can design in 3D from the ground up, making it ideal for developing product components, testing assemblies, and running simulations to validate designs.
Industry Focus
AutoCAD: AutoCAD has cemented its role as the go-to software for architecture, civil engineering, and even some manufacturing processes. It's used to create detailed plans, technical drawings, and even infrastructure layouts, making it a versatile tool for a range of industries that need precise 2D documentation or light 3D visualizations.
Autodesk Inventor: When it comes to mechanical engineering, product design, and prototyping, Inventor takes the lead. The software is designed with manufacturers and engineers in mind, offering tools that help build and test mechanical systems before they ever go into production.
Features and Tools
AutoCAD: AutoCAD excels with its extensive 2D drafting tools, enabling users to create detailed technical drawings with ease. While it does provide some 3D modeling features, they aren’t its primary focus. AutoCAD is more about versatility—used across industries that rely on 2D plans, such as construction, architecture, and urban planning. If you're just getting started with AutoCAD, checking out some of the best AutoCAD courses can help you master its features faster.
Autodesk Inventor: Inventor is built for 3D parametric design, offering advanced tools for creating complex models and assemblies. It also goes beyond just design with its simulation tools, like stress analysis and motion studies. If you need to test how mechanical parts fit and interact before manufacturing, Inventor’s robust capabilities make it the preferred option.
User Interface & Ease of Use
The user interface of any software can greatly impact your efficiency, especially when working on complex designs. Both AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor offer customizable interfaces tailored to their respective uses, but each caters to different types of users. Here’s a look at how their interfaces stack up and what to expect in terms of ease of use.
AutoCAD

Simplicity: AutoCAD’s interface is known for its clean and intuitive layout, especially when it comes to 2D drafting. It’s designed to minimize distractions, so users can focus on creating precise drawings. The interface is straightforward, with easily accessible toolbars and a workspace that prioritizes clarity.
Learning Curve: AutoCAD’s learning curve is relatively gentle, particularly for those working on 2D designs. Beginners can quickly grasp the fundamentals, making it a great choice for new drafters, architects, and designers who need to get up to speed fast.
Customization: AutoCAD’s interface can be highly customized to fit individual workflows. You can arrange tool palettes, create custom commands, and even personalize shortcuts, enabling a tailored user experience that boosts productivity.
Autodesk Inventor

Complexity: In contrast, Autodesk Inventor comes with a feature-rich interface that offers a wide range of tools for 3D modeling, simulation, and assembly. The interface is more detailed, reflecting the complex projects it’s built for, but this can be overwhelming for new users at first.
Learning Curve: Due to its depth of features, Inventor has a steeper learning curve. However, mastering it pays off significantly as it opens the door to powerful 3D parametric modeling and simulation tools, perfect for engineers.
Best for Engineers: Inventor’s interface is specifically designed to meet the needs of engineers, making tasks like technical simulations and mechanical design both intuitive and efficient. If you’re looking to dive into the world of mechanical engineering, Inventor’s UI is crafted to support you.
Performance and File Compatibility
When it comes to performance and file handling, both AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor have distinct strengths, especially in how they manage resources and file formats.
AutoCAD: AutoCAD excels at handling DWG and DXF files, which are the industry standards for 2D drafting. Its lightweight nature means it doesn’t demand a lot from your system, making it ideal for users with moderate hardware setups. If you're using a lower-end device and don't have access to a high-powered GPU, there are ways to optimize AutoCAD’s performance. You can learn more about how to run AutoCAD on low-end devices without a GPU here. Additionally, AutoCAD integrates smoothly with other Autodesk products, ensuring seamless collaboration across different projects. For those looking to maximize efficiency, using AutoCAD on a cloud computer is a great way to work without high-end hardware constraints.
Autodesk Inventor: Inventor, on the other hand, works with more complex file types like IPT, IAM, and IDW, which are necessary for 3D models and mechanical assemblies. Given its advanced simulation and 3D rendering features, Inventor requires more robust computing power. It also supports various mechanical CAD formats such as STEP and IGES, making it highly compatible with industry-standard mechanical files, perfect for engineers and product designers.
Price Comparison
Pricing is another key factor when choosing between AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor. Both follow a subscription-based model, but the cost reflects their feature sets.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is generally more affordable, especially for professionals primarily needing 2D drafting tools. Its pricing is well-suited for architects, drafters, and engineers who don't require advanced 3D capabilities. If your focus is on floor plans, technical drawings, or simple 3D models, AutoCAD offers a cost-effective solution without sacrificing essential design features.
Autodesk Inventor
Autodesk Inventor comes with a higher price tag, but for good reason. Its robust 3D modeling, assembly, and simulation tools provide more advanced capabilities, justifying the cost for mechanical design professionals. While the upfront investment is higher, the return on investment (ROI) is significant for industries needing accurate simulations, stress analysis, and detailed mechanical designs.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between AutoCAD and Autodesk Inventor depends on your specific industry needs and design focus.
Choose AutoCAD If…
You work in architecture or civil engineering.
Your main focus is on precise 2D drafting and technical drawings.
You need an affordable, versatile tool that’s lightweight and widely used across industries.
Choose Autodesk Inventor If…
You’re in mechanical engineering, product design, or manufacturing.
You require advanced 3D parametric modeling and simulation capabilities.
You’re working on complex assemblies or prototypes that need precise testing and analysis.
Final Decision
AutoCAD shines in 2D drafting and versatility, making it a go-to for architects and drafters, while Autodesk Inventor is built for complex 3D mechanical design and simulations, catering to engineers and manufacturers. To find the best fit for your needs, assess your industry demands and project requirements. AutoCAD’s versatility has led to countless amazing designs—see some of the inspiring projects made with AutoCAD that demonstrate its capabilities.
Still unsure? With Vagon, you can test both AutoCAD and Inventor within seconds on cloud-powered computers, ensuring you get the best performance without needing high-end hardware. Once you’ve made your choice, you can also supercharge your workflow and renderings by leveraging Vagon’s cloud computing power—perfect for heavy projects and fast rendering times.
FAQs:
Is AutoCAD or Inventor better for beginners?
For beginners, AutoCAD is typically easier to start with, especially for those focusing on 2D drafting and technical drawings. Its interface is more intuitive for 2D work, while Inventor’s complexity may require more time to master, particularly for 3D modeling.
Can I use AutoCAD for 3D modeling?
Yes, AutoCAD does support 3D modeling, but it’s not as advanced as Inventor. AutoCAD is better suited for simpler 3D projects or visualizations, whereas Inventor specializes in complex 3D designs, assemblies, and simulations.
What industries benefit most from Inventor?
Autodesk Inventor is ideal for industries like mechanical engineering, product design, manufacturing, and aerospace, where creating and testing detailed 3D assemblies and prototypes is essential.
Which software has a steeper learning curve?
Inventor has a steeper learning curve due to its advanced 3D modeling and simulation tools. AutoCAD is more straightforward, particularly for those working in 2D environments.
Is AutoCAD cheaper than Inventor?
Yes, AutoCAD is generally more affordable than Inventor. It’s a good choice for professionals who don’t need advanced 3D capabilities or complex simulations.
Can AutoCAD and Inventor work together?
Absolutely! AutoCAD and Inventor are both Autodesk products, and their files can be easily integrated, making it simple to move between 2D designs in AutoCAD and more detailed 3D work in Inventor.
Get Beyond Your Computer Performance
Run applications on your cloud computer with the latest generation hardware. No more crashes or lags.

Trial includes 1 hour usage + 7 days of storage.
Get Beyond Your Computer Performance
Run applications on your cloud computer with the latest generation hardware. No more crashes or lags.

Trial includes 1 hour usage + 7 days of storage.

Ready to focus on your creativity?
Vagon gives you the ability to create & render projects, collaborate, and stream applications with the power of the best hardware.

Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
How to Use SolidWorks for 3D Printing: STL Export, Settings & Workflow Guide
How to Use Rhino3D for 3D Printing: A Complete Guide to STL, Meshes, and Printable Geometry
Best VMware Horizon Alternatives for VDI Teams in 2026
Top Citrix Alternatives in 2026
Top Azure Virtual Desktop Alternatives in 2026
Best Laptops of 2026: What Actually Matters
Best 3D Printers in 2026: Honest Picks, Real Use Cases
Best AI Productivity Tools in 2026: Build a Smarter Workflow
Best AI Presentation Tools in 2026: What Actually Works
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
How to Use SolidWorks for 3D Printing: STL Export, Settings & Workflow Guide
How to Use Rhino3D for 3D Printing: A Complete Guide to STL, Meshes, and Printable Geometry
Best VMware Horizon Alternatives for VDI Teams in 2026
Top Citrix Alternatives in 2026
Top Azure Virtual Desktop Alternatives in 2026
Best Laptops of 2026: What Actually Matters
Best 3D Printers in 2026: Honest Picks, Real Use Cases
Best AI Productivity Tools in 2026: Build a Smarter Workflow
Best AI Presentation Tools in 2026: What Actually Works
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
How to Use SolidWorks for 3D Printing: STL Export, Settings & Workflow Guide
How to Use Rhino3D for 3D Printing: A Complete Guide to STL, Meshes, and Printable Geometry
Best VMware Horizon Alternatives for VDI Teams in 2026
Top Citrix Alternatives in 2026
Top Azure Virtual Desktop Alternatives in 2026
Best Laptops of 2026: What Actually Matters
Best 3D Printers in 2026: Honest Picks, Real Use Cases
Best AI Productivity Tools in 2026: Build a Smarter Workflow
Best AI Presentation Tools in 2026: What Actually Works
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog


