Instant Connection for Pixel Streaming
— New Feature Automated Setup

AutoCAD vs CATIA: A Beginner’s Guide to Choosing the Right 3D CAD Software
AutoCAD vs CATIA: A Beginner’s Guide to Choosing the Right 3D CAD Software
AutoCAD vs CATIA: A Beginner’s Guide to Choosing the Right 3D CAD Software
Published on September 24, 2024
Table of Contents
Struggling to pick between AutoCAD and CATIA for your design projects? You’re not alone! Choosing the right CAD software can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re just starting. Whether you're crafting detailed architectural plans or designing intricate aerospace components, the tool you select will directly impact the quality and efficiency of your work. If you’ve explored AutoCAD vs SketchUp before, you might be curious how CATIA compares in a more industrial setting. But which one is the best fit for you?
This guide breaks down the key differences between AutoCAD and CATIA to help you make an informed choice. Whether you're an architect, engineer, or aspiring 3D designer, understanding the strengths and limitations of each platform will guide you toward the software that best suits your specific needs. Let’s dive in and simplify your decision-making process.
You can also check out our GPU Guide for tips to use GPU, along with speed up and acceleration tips for Autodesk AutoCAD.
AutoCAD vs CATIA: What’s the Difference?
When comparing AutoCAD and CATIA, it's important to recognize that they are designed with different purposes and industries in mind. While both are giants in the CAD world, they serve distinct user needs.
AutoCAD:
AutoCAD is renowned for its versatility, excelling in 2D drafting with the added capability for basic 3D modeling. It’s particularly popular in fields like architecture, civil engineering, and mechanical design. Many designers debating between AutoCAD vs Rhino find AutoCAD to be an easier starting point due to its intuitive interface and simpler learning curve. AutoCAD’s strength lies in its ease of use, allowing users to jump in quickly without a steep learning curve. For those focused on creating detailed 2D plans, technical drawings, or even experimenting with simple 3D designs, AutoCAD is often the go-to tool.
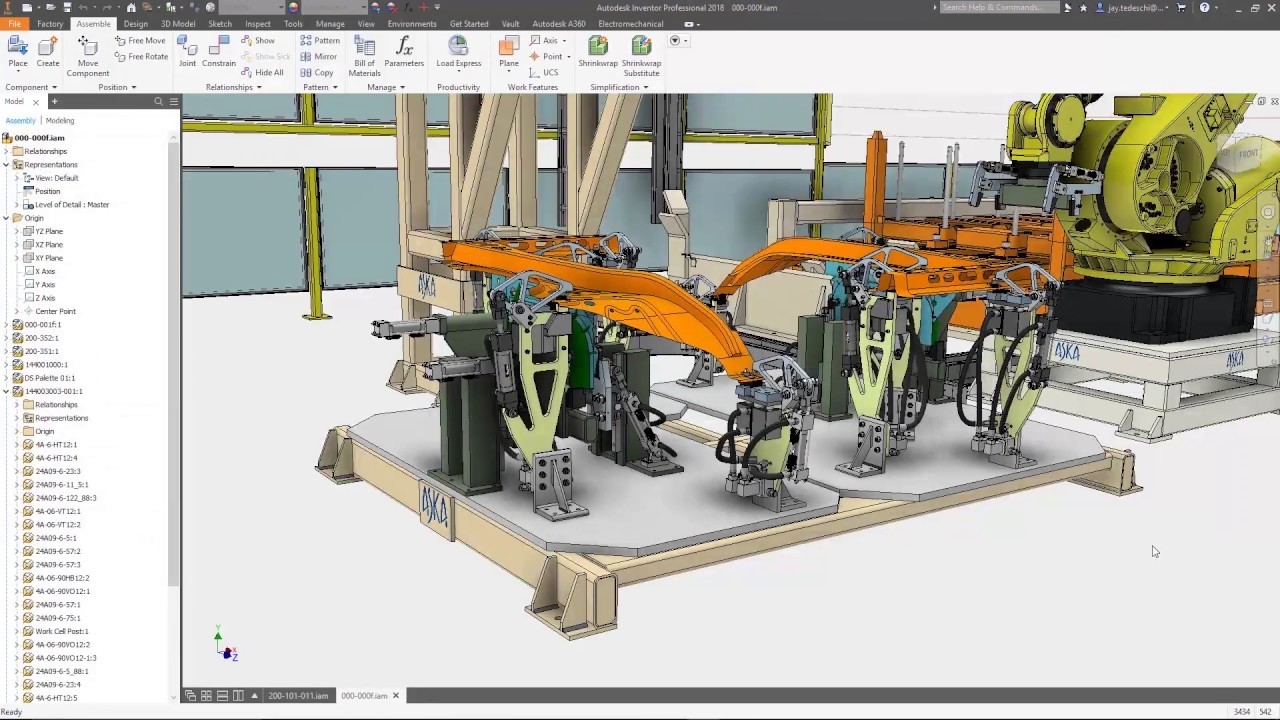
CATIA:
On the other hand, CATIA is a powerhouse for advanced 3D modeling and complex product development. Originally developed for the aerospace industry, it has become the standard in high-precision industries like automotive and industrial machinery design. CATIA’s features go beyond just modeling, integrating tools for simulation, manufacturing, and product lifecycle management (PLM). While it offers unparalleled precision and functionality, it’s also more complex to learn, making it the preferred choice for experienced designers handling large, intricate projects.
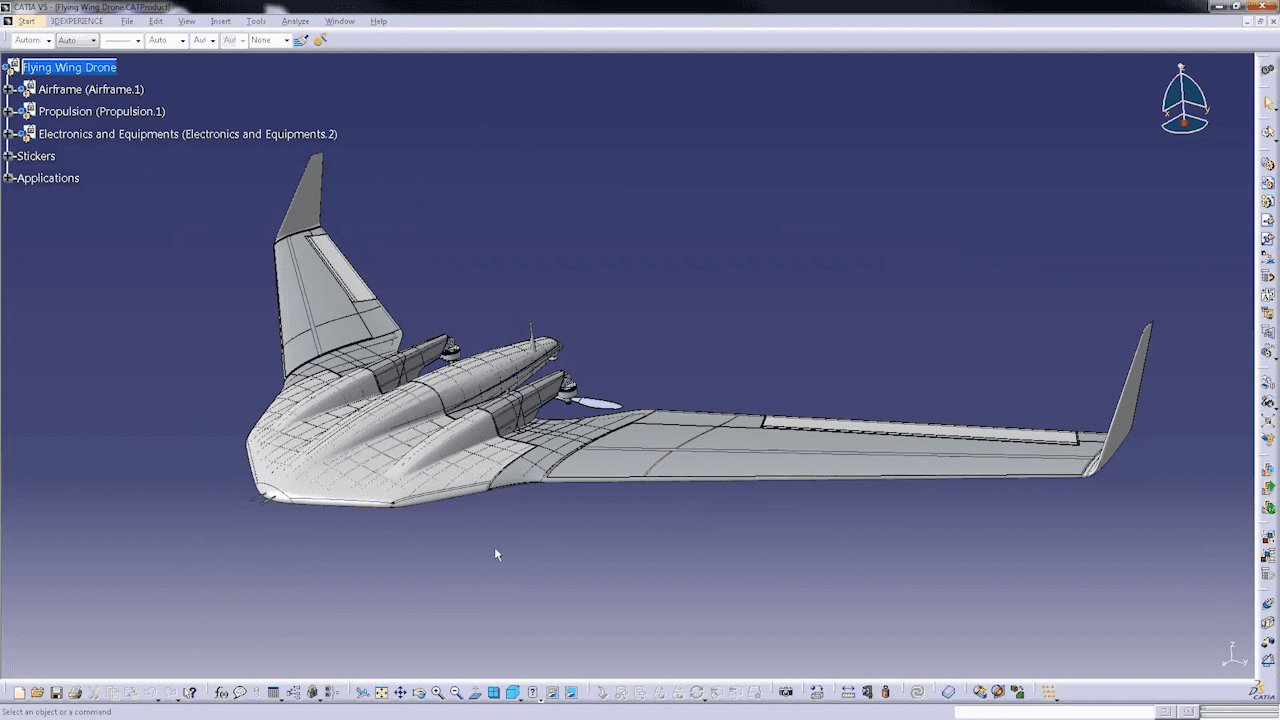
In short, AutoCAD is your choice for simple, accessible design work, while CATIA shines when you need cutting-edge technology for detailed, industry-grade projects.
Feature Comparison: AutoCAD vs CATIA
When choosing between AutoCAD and CATIA, a deep dive into their core features is essential. Each software brings unique strengths to the table, but their capabilities cater to very different design needs. Below, we break down key aspects to help you better understand how each platform performs. For instance, AutoCAD's ease of use makes it a top choice for those considering AutoCAD vs Revit in the architecture world, while CATIA is preferred for complex industrial designs.
Design Capabilities
AutoCAD:
AutoCAD is a master of 2D drafting and also supports basic 3D modeling, making it a versatile choice for a wide range of design tasks. Whether you're sketching out architectural layouts, creating civil engineering plans, or handling MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) systems, AutoCAD’s toolset is both robust and efficient. Its strength lies in its precision and ease of use for creating technical drawings and blueprints, but it also provides enough 3D functionality for simpler models.
CATIA:
For those who need to take their designs to the next level, CATIA offers advanced 3D modeling with exceptional detail and complexity. Whether you're working on surface modeling, solid design, or complex assemblies, CATIA is built to handle intricate projects that require extreme precision. Its integration with PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) tools makes it particularly powerful for industries where design, simulation, and manufacturing are closely linked. It’s the go-to software for engineers who need to model not just a part, but an entire product ecosystem from start to finish.
User Interface & Learning Curve
AutoCAD:
One of AutoCAD's biggest advantages is its simple and intuitive interface. This makes it especially appealing to beginners and intermediate designers. The clean layout and straightforward tools allow users to quickly grasp its functionality, with a wealth of tutorials and community support readily available. AutoCAD’s learning curve is notably shorter, so users can start creating in a relatively short amount of time, making it ideal for those who want to hit the ground running. For those trying out different software, it’s worth comparing AutoCAD vs Inventor or other Autodesk tools to see which suits your needs best.
CATIA:
CATIA, however, presents a more complex and feature-rich interface. While it offers unmatched design depth, the software's intricacies can be challenging for new users. The learning curve is steep, especially for those unfamiliar with high-end 3D modeling or product lifecycle management. CATIA is tailored more for seasoned professionals in specialized fields, where the added complexity is necessary for the detailed work required in sectors like aerospace or automotive engineering.
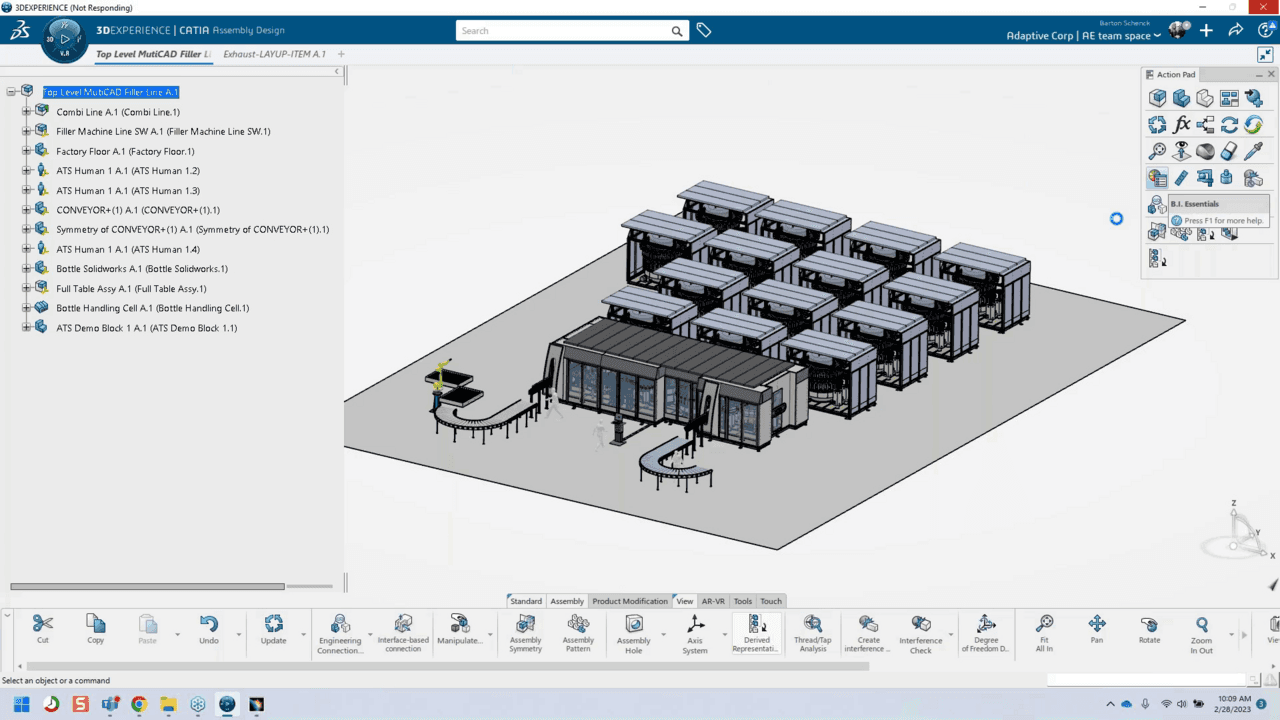
Industry Applications
AutoCAD:
AutoCAD holds a dominant position in fields like architecture, civil engineering, and construction. It’s widely used for creating 2D technical drawings, floor plans, and blueprints, and also works well for generating simple 3D visualizations when necessary. Its flexibility across different project types and industries makes it a top choice for designers focused on building design, infrastructure, and structural plans. Designers who have already explored AutoCAD vs ArchiCAD for building design often find AutoCAD more flexible across various project types.
CATIA:
In contrast, CATIA thrives in industries that demand high levels of precision and complexity. It’s particularly favored by aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing companies for the creation of intricate 3D models. From aircraft components to car body designs, CATIA’s capabilities allow for detailed, large-scale assemblies. Its strength in handling complex geometries and mechanical systems makes it indispensable for companies dealing with highly specialized or industrial-scale projects.
File Compatibility
AutoCAD:
When it comes to file compatibility, AutoCAD offers support for a wide variety of formats, including its native DWG and DXF files. These formats are widely accepted across different industries and can be easily shared with other CAD software, making collaboration smooth and efficient.
CATIA:
CATIA, meanwhile, supports industry-standard formats such as STEP and IGES, which are essential for seamless collaboration with manufacturing and product development teams. These formats allow CATIA to integrate into the broader ecosystem of design, simulation, and manufacturing software, making it highly adaptable to industrial workflows.
Performance: Speed & Efficiency
When it comes to speed and efficiency, AutoCAD and CATIA deliver very different experiences based on the complexity of your projects and the hardware you're using.
AutoCAD:
AutoCAD is designed to be lightweight and efficient, requiring minimal system resources to run smoothly. This makes it a perfect fit for smaller projects and users working with mid-range hardware. Whether you're drafting 2D floor plans or creating simple 3D models, AutoCAD operates swiftly, allowing you to complete tasks without lag or system slowdowns. If you're looking to optimize your hardware for smoother performance, here’s a full breakdown of the best PC for AutoCAD based on project size and usage type. Its quick performance is especially beneficial for those working on tight deadlines or handling multiple smaller projects at once. Those who need a more advanced tool might also explore AutoCAD vs Fusion 360 if they require more 3D capabilities.
CATIA:
On the other hand, CATIA is a heavier, resource-intensive software built for more complex tasks. Its ability to handle large-scale assemblies and intricate product designs comes at the cost of higher system requirements. CATIA thrives on high-end hardware and can struggle on lower-spec machines, especially when dealing with complex models or simulations. For industrial-grade modeling, engineering simulations, or projects involving detailed components, CATIA is unmatched in its ability to handle heavy data loads and deliver smooth performance, but you’ll need the right equipment to fully leverage its capabilities.
Cost & Licensing: Which Is More Affordable?
The cost of software is often a deciding factor for many designers and businesses. Here’s how AutoCAD and CATIA stack up in terms of pricing.
AutoCAD:
AutoCAD operates on a subscription-based model, with prices starting at $210/month or $1,700/year. This pricing makes it a cost-effective option, particularly for small to medium-sized businesses or individual designers. Autodesk also offers generous discounts for students and educators, making AutoCAD more accessible to those just starting their careers. With its affordability and flexible pricing tiers, AutoCAD appeals to a wide range of users, from freelancers to established firms. For more budget-conscious users, considering AutoCAD vs SolidWorks could also provide valuable insights, especially when weighing advanced functionality against cost.
CATIA:
CATIA’s pricing structure is more complex and modular, depending on the features and tools you require. While the price varies, it typically runs much higher than AutoCAD, with costs often reaching into the thousands of dollars annually. CATIA is primarily geared toward large enterprises and specialized industries, where the advanced functionality justifies the investment. For businesses working on high-precision, large-scale projects, the higher price tag is often worth it, but for smaller operations, CATIA may not be as cost-effective.
In the end, the cost-efficiency of each platform depends on the scale and complexity of your projects. AutoCAD is ideal for those seeking a more affordable option for general design work, while CATIA is better suited for businesses that need high-level features and are prepared to invest in them.
Key Strengths & Weaknesses
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of AutoCAD and CATIA is crucial in making the right choice for your projects. Each software has its own set of advantages tailored to different needs.
AutoCAD Strengths:
AutoCAD stands out for its user-friendly interface and wide industry adoption across various fields like architecture, civil engineering, and mechanical design. Its affordability and lightweight nature make it accessible to smaller businesses and individual designers. With extensive resources for learning and community support, AutoCAD is a flexible tool that adapts to multiple design applications, especially for 2D drafting and basic 3D projects.
AutoCAD Weaknesses:
However, AutoCAD's capabilities in 3D modeling are limited, making it less suitable for more complex and detailed designs. It’s best used for straightforward drafting rather than advanced 3D work.
CATIA Strengths:
On the flip side, CATIA excels in advanced 3D modeling, with integrated tools for simulation, design, and manufacturing that make it a powerhouse for complex product development. It’s a go-to solution for industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision and detail are critical.
CATIA Weaknesses:
The trade-off with CATIA is its high cost and steep learning curve. It requires high-end hardware to run efficiently, which can be a barrier for smaller teams or companies.
Which One Should You Choose?
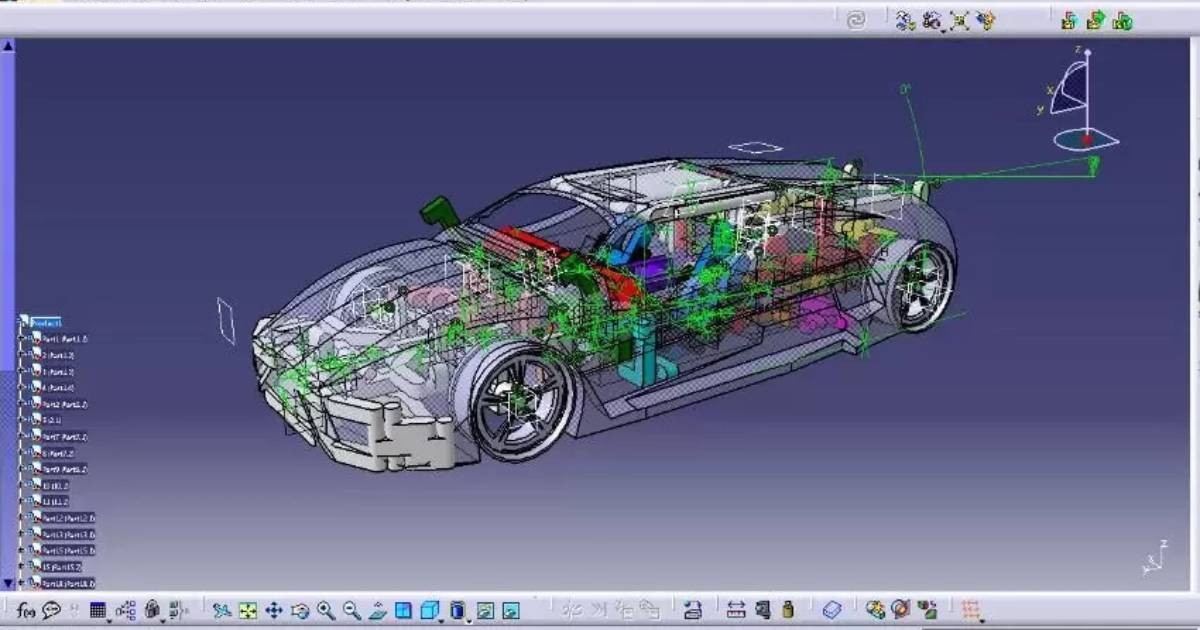
Choosing between AutoCAD and CATIA boils down to the type of projects you’re working on and the resources available to you.
Choose AutoCAD if you primarily focus on 2D drafting or need a tool for simple 3D designs. It’s ideal for projects in architecture, civil engineering, and construction, where ease of use and affordability are key. If you’re a small to medium-sized business or an individual designer looking for a straightforward, easy-to-learn solution, AutoCAD is your best bet. It allows you to get started quickly without a heavy investment in software or hardware.
Choose CATIA if your work involves aerospace, automotive, or other industries where high-precision design and complex simulations are necessary. CATIA is built for handling intricate 3D models and managing large-scale product development projects. However, keep in mind that your organization will need to support the cost and time investment for learning the software and maintaining the necessary hardware. CATIA is perfect for teams that demand a comprehensive, all-in-one solution for advanced product design.
In the end, both tools serve distinct purposes: AutoCAD is the go-to for quick, accessible drafting and basic 3D work, while CATIA is unmatched for those tackling sophisticated design challenges. If you're still on the fence, it's also worth exploring other options in the CAD space. Our guide on the top alternatives to AutoCAD may help you identify the best software for your specific needs.
Final Thoughts: AutoCAD vs CATIA
In conclusion, AutoCAD and CATIA are both powerful tools, but their strengths lie in different areas. AutoCAD excels in 2D drafting and simple 3D designs, making it ideal for architects, civil engineers, and smaller design firms. CATIA, on the other hand, offers advanced 3D capabilities and is built for complex product design, favored by industries like aerospace and automotive.
The choice ultimately depends on the nature of your projects and the industry you work in. Whether you need the flexibility and simplicity of AutoCAD or the precision and depth of CATIA, aligning your software choice with your specific needs is essential.
Want to test both before committing? Try using Vagon to explore both platforms within seconds. With Vagon’s cloud computers, you can experience the full capabilities of AutoCAD and CATIA without the need for high-end hardware. Plus, once you’ve chosen your software, Vagon can power up your workflow and renderings, giving you the performance boost you need to bring your designs to life.
FAQs:
Can AutoCAD be used for 3D modeling?
Yes, AutoCAD supports basic 3D modeling, making it suitable for simple 3D designs. However, for complex and detailed 3D work, other tools like CATIA may be more appropriate.
Is CATIA worth the investment for small design firms?
It depends on the complexity of the projects you handle. CATIA is generally better suited for large-scale, high-precision industries like aerospace or automotive. For smaller firms focused on 2D drafting or simpler 3D work, AutoCAD is often a more cost-effective solution.
How steep is the learning curve for CATIA?
CATIA has a steep learning curve due to its advanced features and complexity. It’s designed for professional use in industries requiring intricate design and simulations, so mastering it takes time and effort.
What industries commonly use AutoCAD?
AutoCAD is widely used in architecture, civil engineering, construction, and mechanical design. Its 2D drafting capabilities make it popular for creating blueprints, technical drawings, and schematics.
Do AutoCAD and CATIA offer free trials or student licenses?
Yes, both AutoCAD and CATIA offer student licenses and free trials for professionals and businesses, making it easy to test their features before committing.
Can I run AutoCAD and CATIA on the same computer?
Yes, both programs can run on the same machine, but CATIA’s higher hardware requirements mean you’ll need a powerful computer to run it smoothly, especially for larger projects. Alternatively, using Vagon’s cloud computers can help run both seamlessly without investing in expensive hardware.
Struggling to pick between AutoCAD and CATIA for your design projects? You’re not alone! Choosing the right CAD software can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re just starting. Whether you're crafting detailed architectural plans or designing intricate aerospace components, the tool you select will directly impact the quality and efficiency of your work. If you’ve explored AutoCAD vs SketchUp before, you might be curious how CATIA compares in a more industrial setting. But which one is the best fit for you?
This guide breaks down the key differences between AutoCAD and CATIA to help you make an informed choice. Whether you're an architect, engineer, or aspiring 3D designer, understanding the strengths and limitations of each platform will guide you toward the software that best suits your specific needs. Let’s dive in and simplify your decision-making process.
You can also check out our GPU Guide for tips to use GPU, along with speed up and acceleration tips for Autodesk AutoCAD.
AutoCAD vs CATIA: What’s the Difference?
When comparing AutoCAD and CATIA, it's important to recognize that they are designed with different purposes and industries in mind. While both are giants in the CAD world, they serve distinct user needs.
AutoCAD:
AutoCAD is renowned for its versatility, excelling in 2D drafting with the added capability for basic 3D modeling. It’s particularly popular in fields like architecture, civil engineering, and mechanical design. Many designers debating between AutoCAD vs Rhino find AutoCAD to be an easier starting point due to its intuitive interface and simpler learning curve. AutoCAD’s strength lies in its ease of use, allowing users to jump in quickly without a steep learning curve. For those focused on creating detailed 2D plans, technical drawings, or even experimenting with simple 3D designs, AutoCAD is often the go-to tool.

CATIA:
On the other hand, CATIA is a powerhouse for advanced 3D modeling and complex product development. Originally developed for the aerospace industry, it has become the standard in high-precision industries like automotive and industrial machinery design. CATIA’s features go beyond just modeling, integrating tools for simulation, manufacturing, and product lifecycle management (PLM). While it offers unparalleled precision and functionality, it’s also more complex to learn, making it the preferred choice for experienced designers handling large, intricate projects.

In short, AutoCAD is your choice for simple, accessible design work, while CATIA shines when you need cutting-edge technology for detailed, industry-grade projects.
Feature Comparison: AutoCAD vs CATIA
When choosing between AutoCAD and CATIA, a deep dive into their core features is essential. Each software brings unique strengths to the table, but their capabilities cater to very different design needs. Below, we break down key aspects to help you better understand how each platform performs. For instance, AutoCAD's ease of use makes it a top choice for those considering AutoCAD vs Revit in the architecture world, while CATIA is preferred for complex industrial designs.
Design Capabilities
AutoCAD:
AutoCAD is a master of 2D drafting and also supports basic 3D modeling, making it a versatile choice for a wide range of design tasks. Whether you're sketching out architectural layouts, creating civil engineering plans, or handling MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) systems, AutoCAD’s toolset is both robust and efficient. Its strength lies in its precision and ease of use for creating technical drawings and blueprints, but it also provides enough 3D functionality for simpler models.
CATIA:
For those who need to take their designs to the next level, CATIA offers advanced 3D modeling with exceptional detail and complexity. Whether you're working on surface modeling, solid design, or complex assemblies, CATIA is built to handle intricate projects that require extreme precision. Its integration with PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) tools makes it particularly powerful for industries where design, simulation, and manufacturing are closely linked. It’s the go-to software for engineers who need to model not just a part, but an entire product ecosystem from start to finish.
User Interface & Learning Curve
AutoCAD:
One of AutoCAD's biggest advantages is its simple and intuitive interface. This makes it especially appealing to beginners and intermediate designers. The clean layout and straightforward tools allow users to quickly grasp its functionality, with a wealth of tutorials and community support readily available. AutoCAD’s learning curve is notably shorter, so users can start creating in a relatively short amount of time, making it ideal for those who want to hit the ground running. For those trying out different software, it’s worth comparing AutoCAD vs Inventor or other Autodesk tools to see which suits your needs best.
CATIA:
CATIA, however, presents a more complex and feature-rich interface. While it offers unmatched design depth, the software's intricacies can be challenging for new users. The learning curve is steep, especially for those unfamiliar with high-end 3D modeling or product lifecycle management. CATIA is tailored more for seasoned professionals in specialized fields, where the added complexity is necessary for the detailed work required in sectors like aerospace or automotive engineering.

Industry Applications
AutoCAD:
AutoCAD holds a dominant position in fields like architecture, civil engineering, and construction. It’s widely used for creating 2D technical drawings, floor plans, and blueprints, and also works well for generating simple 3D visualizations when necessary. Its flexibility across different project types and industries makes it a top choice for designers focused on building design, infrastructure, and structural plans. Designers who have already explored AutoCAD vs ArchiCAD for building design often find AutoCAD more flexible across various project types.
CATIA:
In contrast, CATIA thrives in industries that demand high levels of precision and complexity. It’s particularly favored by aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing companies for the creation of intricate 3D models. From aircraft components to car body designs, CATIA’s capabilities allow for detailed, large-scale assemblies. Its strength in handling complex geometries and mechanical systems makes it indispensable for companies dealing with highly specialized or industrial-scale projects.
File Compatibility
AutoCAD:
When it comes to file compatibility, AutoCAD offers support for a wide variety of formats, including its native DWG and DXF files. These formats are widely accepted across different industries and can be easily shared with other CAD software, making collaboration smooth and efficient.
CATIA:
CATIA, meanwhile, supports industry-standard formats such as STEP and IGES, which are essential for seamless collaboration with manufacturing and product development teams. These formats allow CATIA to integrate into the broader ecosystem of design, simulation, and manufacturing software, making it highly adaptable to industrial workflows.
Performance: Speed & Efficiency

When it comes to speed and efficiency, AutoCAD and CATIA deliver very different experiences based on the complexity of your projects and the hardware you're using.
AutoCAD:
AutoCAD is designed to be lightweight and efficient, requiring minimal system resources to run smoothly. This makes it a perfect fit for smaller projects and users working with mid-range hardware. Whether you're drafting 2D floor plans or creating simple 3D models, AutoCAD operates swiftly, allowing you to complete tasks without lag or system slowdowns. If you're looking to optimize your hardware for smoother performance, here’s a full breakdown of the best PC for AutoCAD based on project size and usage type. Its quick performance is especially beneficial for those working on tight deadlines or handling multiple smaller projects at once. Those who need a more advanced tool might also explore AutoCAD vs Fusion 360 if they require more 3D capabilities.
CATIA:
On the other hand, CATIA is a heavier, resource-intensive software built for more complex tasks. Its ability to handle large-scale assemblies and intricate product designs comes at the cost of higher system requirements. CATIA thrives on high-end hardware and can struggle on lower-spec machines, especially when dealing with complex models or simulations. For industrial-grade modeling, engineering simulations, or projects involving detailed components, CATIA is unmatched in its ability to handle heavy data loads and deliver smooth performance, but you’ll need the right equipment to fully leverage its capabilities.
Cost & Licensing: Which Is More Affordable?
The cost of software is often a deciding factor for many designers and businesses. Here’s how AutoCAD and CATIA stack up in terms of pricing.
AutoCAD:
AutoCAD operates on a subscription-based model, with prices starting at $210/month or $1,700/year. This pricing makes it a cost-effective option, particularly for small to medium-sized businesses or individual designers. Autodesk also offers generous discounts for students and educators, making AutoCAD more accessible to those just starting their careers. With its affordability and flexible pricing tiers, AutoCAD appeals to a wide range of users, from freelancers to established firms. For more budget-conscious users, considering AutoCAD vs SolidWorks could also provide valuable insights, especially when weighing advanced functionality against cost.
CATIA:
CATIA’s pricing structure is more complex and modular, depending on the features and tools you require. While the price varies, it typically runs much higher than AutoCAD, with costs often reaching into the thousands of dollars annually. CATIA is primarily geared toward large enterprises and specialized industries, where the advanced functionality justifies the investment. For businesses working on high-precision, large-scale projects, the higher price tag is often worth it, but for smaller operations, CATIA may not be as cost-effective.
In the end, the cost-efficiency of each platform depends on the scale and complexity of your projects. AutoCAD is ideal for those seeking a more affordable option for general design work, while CATIA is better suited for businesses that need high-level features and are prepared to invest in them.
Key Strengths & Weaknesses
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of AutoCAD and CATIA is crucial in making the right choice for your projects. Each software has its own set of advantages tailored to different needs.
AutoCAD Strengths:
AutoCAD stands out for its user-friendly interface and wide industry adoption across various fields like architecture, civil engineering, and mechanical design. Its affordability and lightweight nature make it accessible to smaller businesses and individual designers. With extensive resources for learning and community support, AutoCAD is a flexible tool that adapts to multiple design applications, especially for 2D drafting and basic 3D projects.
AutoCAD Weaknesses:
However, AutoCAD's capabilities in 3D modeling are limited, making it less suitable for more complex and detailed designs. It’s best used for straightforward drafting rather than advanced 3D work.
CATIA Strengths:
On the flip side, CATIA excels in advanced 3D modeling, with integrated tools for simulation, design, and manufacturing that make it a powerhouse for complex product development. It’s a go-to solution for industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision and detail are critical.
CATIA Weaknesses:
The trade-off with CATIA is its high cost and steep learning curve. It requires high-end hardware to run efficiently, which can be a barrier for smaller teams or companies.
Which One Should You Choose?

Choosing between AutoCAD and CATIA boils down to the type of projects you’re working on and the resources available to you.
Choose AutoCAD if you primarily focus on 2D drafting or need a tool for simple 3D designs. It’s ideal for projects in architecture, civil engineering, and construction, where ease of use and affordability are key. If you’re a small to medium-sized business or an individual designer looking for a straightforward, easy-to-learn solution, AutoCAD is your best bet. It allows you to get started quickly without a heavy investment in software or hardware.
Choose CATIA if your work involves aerospace, automotive, or other industries where high-precision design and complex simulations are necessary. CATIA is built for handling intricate 3D models and managing large-scale product development projects. However, keep in mind that your organization will need to support the cost and time investment for learning the software and maintaining the necessary hardware. CATIA is perfect for teams that demand a comprehensive, all-in-one solution for advanced product design.
In the end, both tools serve distinct purposes: AutoCAD is the go-to for quick, accessible drafting and basic 3D work, while CATIA is unmatched for those tackling sophisticated design challenges. If you're still on the fence, it's also worth exploring other options in the CAD space. Our guide on the top alternatives to AutoCAD may help you identify the best software for your specific needs.
Final Thoughts: AutoCAD vs CATIA
In conclusion, AutoCAD and CATIA are both powerful tools, but their strengths lie in different areas. AutoCAD excels in 2D drafting and simple 3D designs, making it ideal for architects, civil engineers, and smaller design firms. CATIA, on the other hand, offers advanced 3D capabilities and is built for complex product design, favored by industries like aerospace and automotive.
The choice ultimately depends on the nature of your projects and the industry you work in. Whether you need the flexibility and simplicity of AutoCAD or the precision and depth of CATIA, aligning your software choice with your specific needs is essential.
Want to test both before committing? Try using Vagon to explore both platforms within seconds. With Vagon’s cloud computers, you can experience the full capabilities of AutoCAD and CATIA without the need for high-end hardware. Plus, once you’ve chosen your software, Vagon can power up your workflow and renderings, giving you the performance boost you need to bring your designs to life.
FAQs:
Can AutoCAD be used for 3D modeling?
Yes, AutoCAD supports basic 3D modeling, making it suitable for simple 3D designs. However, for complex and detailed 3D work, other tools like CATIA may be more appropriate.
Is CATIA worth the investment for small design firms?
It depends on the complexity of the projects you handle. CATIA is generally better suited for large-scale, high-precision industries like aerospace or automotive. For smaller firms focused on 2D drafting or simpler 3D work, AutoCAD is often a more cost-effective solution.
How steep is the learning curve for CATIA?
CATIA has a steep learning curve due to its advanced features and complexity. It’s designed for professional use in industries requiring intricate design and simulations, so mastering it takes time and effort.
What industries commonly use AutoCAD?
AutoCAD is widely used in architecture, civil engineering, construction, and mechanical design. Its 2D drafting capabilities make it popular for creating blueprints, technical drawings, and schematics.
Do AutoCAD and CATIA offer free trials or student licenses?
Yes, both AutoCAD and CATIA offer student licenses and free trials for professionals and businesses, making it easy to test their features before committing.
Can I run AutoCAD and CATIA on the same computer?
Yes, both programs can run on the same machine, but CATIA’s higher hardware requirements mean you’ll need a powerful computer to run it smoothly, especially for larger projects. Alternatively, using Vagon’s cloud computers can help run both seamlessly without investing in expensive hardware.
Get Beyond Your Computer Performance
Run applications on your cloud computer with the latest generation hardware. No more crashes or lags.

Trial includes 1 hour usage + 7 days of storage.
Get Beyond Your Computer Performance
Run applications on your cloud computer with the latest generation hardware. No more crashes or lags.

Trial includes 1 hour usage + 7 days of storage.

Ready to focus on your creativity?
Vagon gives you the ability to create & render projects, collaborate, and stream applications with the power of the best hardware.

Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
Best VMware Horizon Alternatives for VDI Teams in 2026
Top Citrix Alternatives in 2026
Top Azure Virtual Desktop Alternatives in 2026
Best Laptops of 2026: What Actually Matters
Best 3D Printers in 2026: Honest Picks, Real Use Cases
Best AI Productivity Tools in 2026: Build a Smarter Workflow
Best AI Presentation Tools in 2026: What Actually Works
Best Video Editing Software in 2026: Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve & More
The Best AI Video Generators in 2026: Tested Tools, Real Results
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
Best VMware Horizon Alternatives for VDI Teams in 2026
Top Citrix Alternatives in 2026
Top Azure Virtual Desktop Alternatives in 2026
Best Laptops of 2026: What Actually Matters
Best 3D Printers in 2026: Honest Picks, Real Use Cases
Best AI Productivity Tools in 2026: Build a Smarter Workflow
Best AI Presentation Tools in 2026: What Actually Works
Best Video Editing Software in 2026: Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve & More
The Best AI Video Generators in 2026: Tested Tools, Real Results
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog
Best VMware Horizon Alternatives for VDI Teams in 2026
Top Citrix Alternatives in 2026
Top Azure Virtual Desktop Alternatives in 2026
Best Laptops of 2026: What Actually Matters
Best 3D Printers in 2026: Honest Picks, Real Use Cases
Best AI Productivity Tools in 2026: Build a Smarter Workflow
Best AI Presentation Tools in 2026: What Actually Works
Best Video Editing Software in 2026: Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve & More
The Best AI Video Generators in 2026: Tested Tools, Real Results
Vagon Blog
Run heavy applications on any device with
your personal computer on the cloud.
San Francisco, California
Solutions
Vagon Teams
Vagon Streams
Use Cases
Resources
Vagon Blog


